A restriction in genetic variability caused by a drastic reduction in population size is called a
A. Hardy-Weinberg effect.
B. polymorphic effect.
C. adaptive effect.
D. bottleneck effect.
E. founder effect.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
An organism that contains patches of tissue that vary for a specific characteristic such as a pigment, can be an example of which of the following?
A. Linkage B. Meiotic recombination C. Mitotic recombination D. Translocations E. None of the answers are correct
Oak trees and many other plant species have years in which they have synchronous production of many progeny by all individuals in a population. This is known as
A. sympatry. B. crypsis. C. semelparity. D. masting.
The nuclear condition (ploidy) that club fungi
spend most of their lives in is
a. diploid. b. haploid. c. dikaryotic. d. mycokaryotic. e. triploid.
The associated figure provides support for which of the following processes?
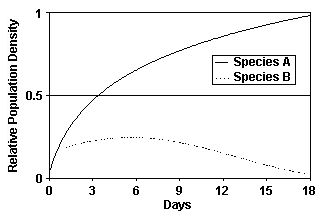
a. secondary succession
b. competitive exclusion
c. coevolution
d. mutualism
e. resource partitioning