Which of the following is not likely to contribute to economic growth?
A. Technological development
B. Government planning
C. Institutions with incentives compatible with growth
D. Entrepreneurship
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Which one of the following resources is not underemployed?
A. The use of Manhattan Island in New York City for growing corn. B. The use of farmland in the Iowa and Illinois corn belt for buildings to do stock market research. C. An automobile factory that is shut down for two months to be retooled for a model change. D. Limiting all men to the fields of school teaching and social work.
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as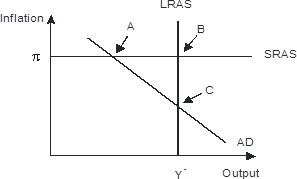
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward C. Aggregate demand shifting rightward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
Why do airlines often charge students and vacationers a lower price than business travelers?
a. It is cheaper to provide airline service to students and vacationers than to business travelers. b. The demand of business travelers is generally more elastic than the demand of students and vacationers. c. The demand of students and vacationers is generally more elastic than the demand of business travelers. d. Airlines prefer to deal with students and vacationers rather than business travelers.
Which of the following statements is true about the Canadian health care system?
a. Almost 50,000 Canadians travel abroad each year to avoid waiting lists for services. b. Canadian physicians are salaried employees of the provincial health plans. c. Canadians have the option of purchasing private health insurance if they can afford it. d. Canadian physicians are allowed to "balance bill" patients for certain high-cost procedures. e. Canadian hospitals have significant excess capacity that is used to treat patients from foreign countries.