Demand is given by QD = 6000 - 50P. Domestic supply is QS = 25P. Foreign producers can supply any quantity at a price of $40
a. If foreign producers can sell in the domestic market, what is the equilibrium price? What is the equilibrium quantity? How much is sold by domestic and foreign producers, respectively?
b. Under domestic government pressure, foreign producers voluntarily agree to restrict their goods. What will happen to the price and quantity? What will happen to the amount that domestic producers supply? What will happen to revenues of domestic and foreign producers?
a. P = $40. Q = 4,000. Of that, domestic producers supply 1,000 units, and foreign producers supply 3,000 units.
b. The quantity restriction will cause equilibrium price to rise and quantity to decrease. Domestic producers will sell more, and foreign producers will sell less. Revenues of domestic producers will rise. The effect on the revenues of foreign producers is unclear; if demand is inelastic, they may rise.
You might also like to view...
Consider the following pairs of items:
a. shampoo and conditioner b. iPhones and earbuds c. a laptop computer and a desktop computer d. beef and pork e. air-travel and weed killer Which of the pairs listed will have a negative cross-price elasticity? A) a and b only B) c and d only C) e only D) a, b, and c only
Open market purchases ________ reserves and the monetary base thereby ________ the money supply
A) raise; lowering B) raise; raising C) lower; lowering D) lower; raising
The nominal exchange rate:
A. expresses the value of goods in one country in terms of the same goods in another country. B. expresses the value of goods in one country in terms of another country's currency. C. is the stated rate at which one country's currency can be traded for another country's goods and services. D. is the stated rate at which one country's currency can be traded for another country's currency.
A move from G to H represents
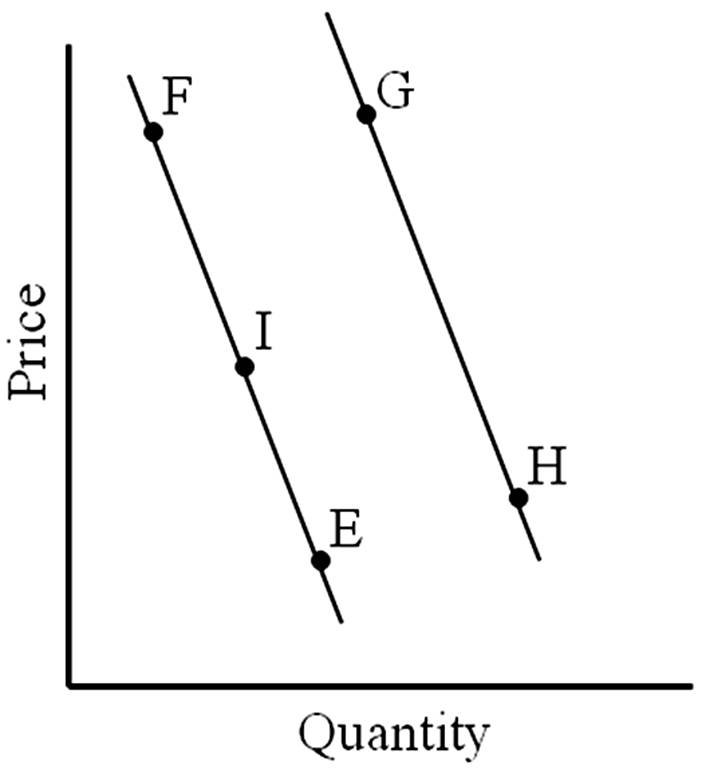
A. a change in quantity demanded.
B. a change in demand.
C. an increase in demand.
D. a decrease in demand.