What is the ideological position of the median voter in Figure 1?
Figure 1 illustrates an election in which there are seven voters (A, B, C, D, E, F, G) arrayed along a single left–right issue dimension that runs from 0 (most left) to 10 (most right). Each voter is assumed to have a single-peaked preference ordering over the issue dimension and to vote for the party that is located closest to her ideal point. The voters are participating in a majority rule election in which there are two parties, P1 and P2, competing for office.These parties can be thought of as “office-seeking” parties since they only care about winning the election and getting into office.
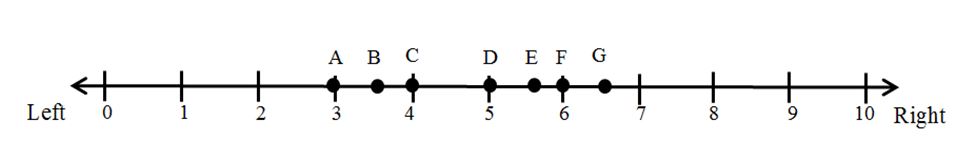
A. 1.5
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
F. 5.5
G. 7
H. 8
D. 4
You might also like to view...
Since independence, Nigeria has had all of the following types of regimes EXCEPT a. semipresidentialism. b. presidentialism
c. parliamentarianism. d. direct military rule. e. authoritarianism.
Most states, including Texas, no longer have unenforceable constitutional and statutory provisions that conflict with federal laws
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
The best example of the generational effect is
A) individuals who are in their early twenties tend to have more liberal attitudes toward social issues. B) candidate Hillary Clinton received significant support from women in the 2016 presidential campaign. C) many individuals remember where they were the night Barack Obama was first elected. D) individuals who came of age during the Watergate scandal have a cynical attitude toward government. E) individuals with a high economic status tend to be more politically involved.
__________ have historically had very low participation rates in elections.
A. Middle class B. Men with a high school education C. Senior citizens D. Hispanics