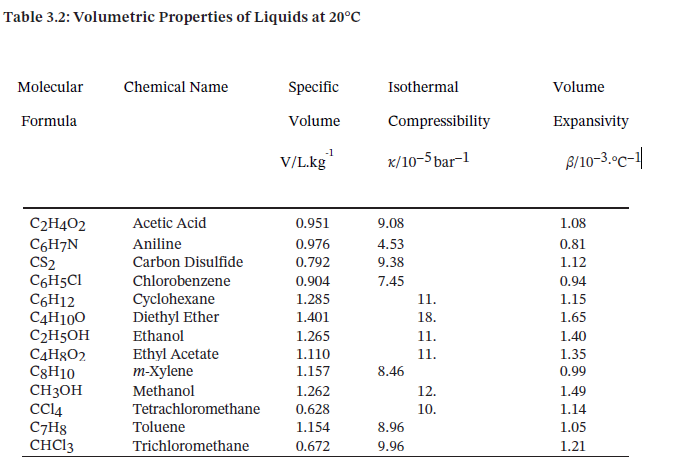
For one of the substances in Table 3.2, compute the change in volume and work done when one kilogram of the substance is compressed from 1 bar to 100 bar at a constant temperature of 20°C.
Table 3.2 provides the specific volume, isothermal compressibility, and volume expansivity of several liquids at 20°C and 1 bar25, where ? and ? may be assumed constant.
First ethanol will be chosen as the substance to be used. In the problem the temperature is held constant, then the isothermal compressibility equation is used to determine the change in volume.
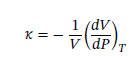
Solving for dv and integrating gives:
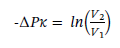
Solving for V2 gives:
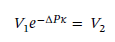
Plugging in the specific volume and isothermal compressibility factor leads V2 = 1.251 L for 1 kilogram of ethanol.
To determine the work we know that:
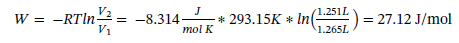
You might also like to view...
Elevator and stair shafts in building cores are often constructed by using a type of _____.
a. sliding form b. climbing form c. slip form d. jack-raised form
Two technicians are discussing torque wrenches. Technician A says that a torque wrench is capable of tightening a fastener with more torque than a conventional breaker bar or ratchet. Technician B says that a torque wrench should be calibrated regularly for the most accurate results. Which technician is correct?
A) Technician A only B) Technician B only C) Both technicians D) Neither technician
Hellenistic economies were predominantly
a. commercial. b. industrial. c. agricultural. d. maritime.
Which of the following types of energy are radiated from a perfect blackbody?
A. emitted B. reflected C. transmitted D. all of the above