With free trade the United States imports about half of its steel consumption from China. Show this graphically, using a graph of the U.S. national market for steel (including both domestic steel supply and imported steel supply), and explain the impact on the United States of an export subsidy on steel provided by the Chinese government. (Assume the Chinese export subsidy lowers the price that Chinese steel exporters charge.) Would it be beneficial for the United States to impose an equal amount of countervailing duty on the import of steel? Why or why not?
What will be an ideal response?
POSSIBLE RESPONSE: To evaluate the impact of the export subsidy provided by the Chinese government, let's first take a look at the diagram below which illustrates the U.S. market for steel.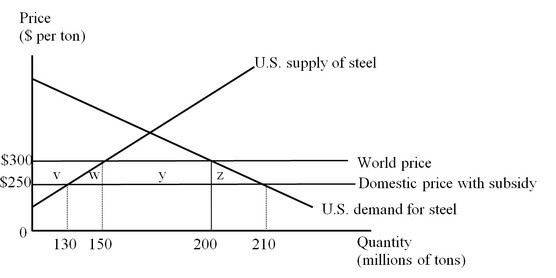
Let's assume the current world price is $300 per ton. After the Chinese government provides a subsidy to steel exports, the price of the imported steel in the U.S. market falls to $250. Steel consumers in the United States gain an additional consumer surplus equal to the area (v + w + y + z). Producers lose a surplus equal to the area 'v'. So, the net benefit to the United States from the Chinese export subsidy is represented by the area (w + y + z).
If the U.S. government decides to impose a countervailing duty on the imports of Chinese steel to offset the impact of the subsidy, the price of the imported steel in the U.S. market climbs back to the initial level of $300 per ton. The steel producers in the United States get back their lost surplus as shown by the area 'v'. The U.S. consumers on the other hand, lose surplus given by the area (v + w + y + z). The U.S. government collects tariff revenue equal to the area 'y'. From the figure we can conclude that the countervailing duty lowers welfare in the United States by the area (w + z). Thus, imposing a countervailing duty would actually harm the U.S. economy.
You might also like to view...
Macroeconomic equilibrium occurs when
A) there is no inflation. B) real GDP is equal to potential GDP. C) the aggregate quantity demanded is equal to the aggregate quantity supplied. D) the economy is fully employed. E) the price level equals the potential price level.
The opportunity cost of something you decide to get is
A) all the possible alternatives that you give up to get it. B) the highest valued alternative you give up to get it. C) the value of the item minus the cost you paid for it. D) the amount of money you pay to get it.
When the United States exports a good, the amount of the ________ in U.S. consumer surplus is ________ the amount of the ________ in U.S. producer surplus
A) increase; smaller than; increase B) increase; larger than; decrease C) decrease; smaller than; increase D) decrease; equal to; decrease
Consider the monopsony in the above figure. The monopsony will hire ________ hours per week
A) 200 B) 400 C) 600 D) None of the above answers is correct.