Lichens dominate in extreme environments
What will be an ideal response?
-Hold moisture
-Protect seeds
-Prevent erosion
-Input N
You might also like to view...
Recombination between homologous chromosomes:
A. can lead to a gene conversion event if the region between the two Holliday intermediates contains base pair differences. B. uses extended synthesis-dependent strand annealing (ESDSA) rather than synthesis-dependent strand annealing (SDSA). C. can occur at completely random sites on the chromosome; there is no apparent regulation of the process. D. occurs between sister chromatids and nonsister chromatids with equal frequency. E. None of the choices given is true.
What nucleotide change is a shared derived character for species A, B, and C, but not for species G?
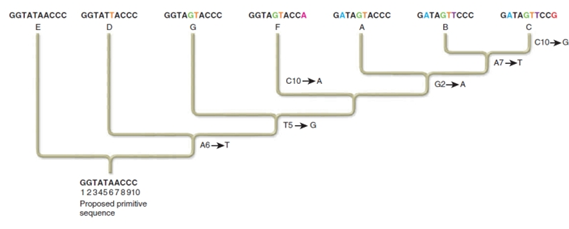
A,T,G, and C refer to nucleotide bases, and the numbers refer to the position of the base in the nucleotide sequences.
For example, A6 refers to an adenine at the sixth position.
A. Changing the second G to an A is common to species A, B, and C, but not to species G.
B. Changing the fifth T to a G is common to species A, B, and C, but not to species G.
C. Changing the second G to a T is common to species A, B, and C, but not to species G.
D. Changing the second G to an A and the fifth T to a G is common to species A, B, and C, but not to species G.
E. None of these show a change in derived characteristics for A, B, and C that are not found in G.
Which type of species is most likely to go extinct?
a. underharvested b. endemic c. widely distributed d. generalist e. introduced
One of the advantages of STR profiling over VNTR profiling is that ________
A) STRs are variable in the number of repeats, whereas VNTRs are not B) it presents more variable sequences reducing false positive matches C) STRs are not variable in the number of repeats, whereas VNTRs are D) it requires much less DNA because PCR can be used to amplify small samples