Clark enjoys fishing and hunting. He divides his leisure hours between the two outdoor activities. Suppose we were to draw Clark's indifference curves for the two activities, placing fishing on the horizontal axis and hunting on the vertical axis. If Clark's indifference curves are bowed inward, then
a. the rate at which he is willing to give up an hour of hunting for an hour of fishing changes depending on how many hours of each activity he has done. For example, if Clark has already fished a lot in one week, he will be more willing to give up an hour of fishing for an hour of hunting than if he has only fished a little that week.
b. the rate at which he is willing to give up an hour of hunting for an hour of fishing is constant because he must derive the same enjoyment out of each activity.
c. the rate at which he is willing to give up an hour of hunting for an hour of fishing changes depending on how many hours of each activity he has done. For example, if Clark has already fished a lot in one week, he will be less willing to give up an hour of fishing for an hour of hunting than if he has only fished a little that week.
d. Clark's indifference curves will not cross. When indifference curves are bowed outward, the indifference curves must cross.
a
You might also like to view...
A school teacher gets paid today in money, but plans to spend the money in six months on a vacation. This illustrates which function of money?
A) medium of exchange B) store of value C) standard of value D) serving as a commodity
Made in the USA or Made in China has less meaning for products that
A) are a commodity such as iron ore. B) are an agricultural product such as wheat. C) are a product that is technological and involves assembling many different types of sometimes sophisticated components. D) are a product that is produced and consumed domestically. E) were produced fifty years ago versus the types of products manufactured today.
The alternative combinations of goods and services that can be produced in a given time period with the available resources and technology is the:
A. Production possibilities. B. Consumption possibilities. C. International trade balance. D. Comparative advantage.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 13.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 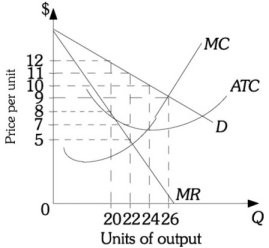 Figure 13.4Refer to Figure 13.4. The profit-maximizing level of output for this monopolist is ________ units of output.
Figure 13.4Refer to Figure 13.4. The profit-maximizing level of output for this monopolist is ________ units of output.
A. 20 B. 22 C. 24 D. 26