Refer to Figure 9.4. In the long run, how much should the firm produce at the price P3?
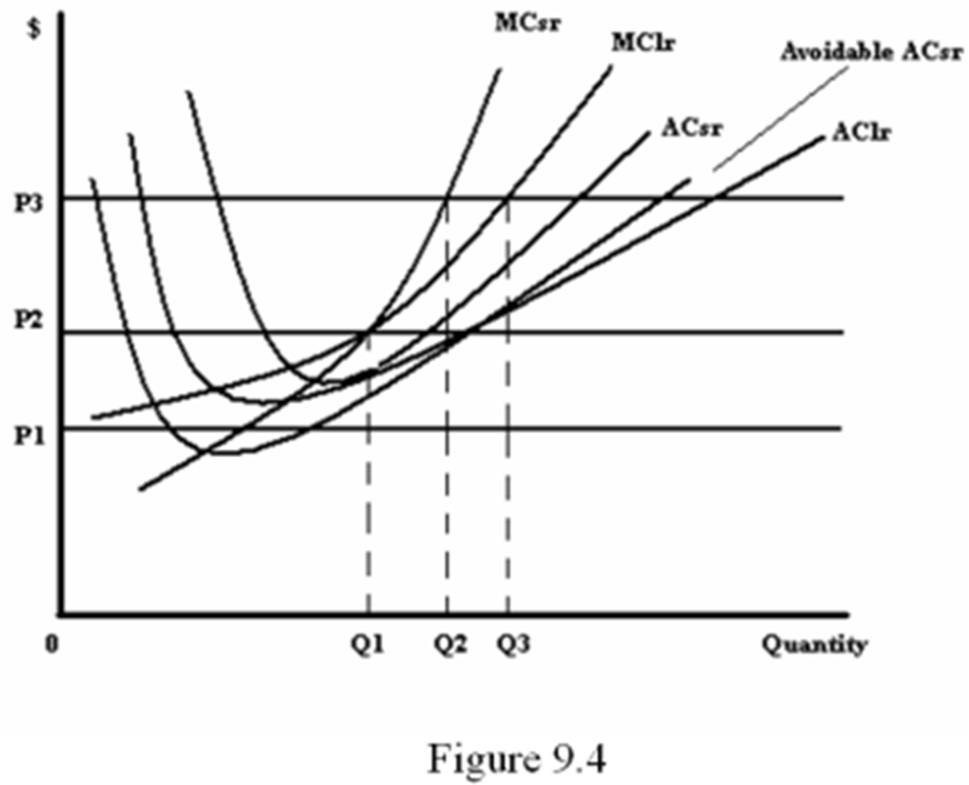
A. 0
B. Q1
C. Q2
D. Q3
D. Q3
You might also like to view...
During the 1990s, food production increased faster than population in all regions of the developing world except
(a) Latin America. (b) East Asia. (c) Sub-Saharan Africa. (d) none of the above.
Consider the following: Farmer Jones bought seed and fertilizer for $100. He grew wheat that he sold to the Acme Bread Company for $200. Acme Bread produced and sold bread to the ABC Grocery Store for $250. Consumers bought the bread from the grocery for $350. How much was added to the GDP?
Refer to the table below. If the profit for each unit of paper product is $2 and the profit for each unit of lumber is $5, what is the marginal benefit for each unit of lumber produced?
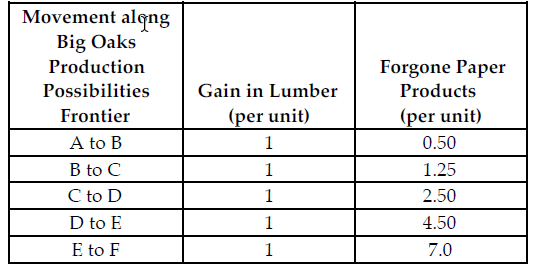
Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amount of paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable proportions. The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.
A) $3
B) $7
C) $2
D) $5
Excess capacity is defined as the difference between a firm's maximum possible output and its actual output
a. True b. False