An increase in technology ________ potential GDP and ________ aggregate supply
A) increases; increases
B) increases; decreases
C) decreases; increases
D) decreases; decreases
E) does not change; does not change
A
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as 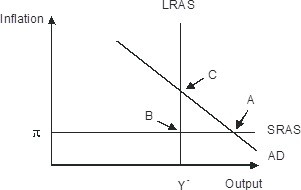
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting upward C. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
The above figure shows the marginal private benefit and marginal social cost of a college education. If society's external benefits from college graduates is $10,000 each, then the
A) marginal social cost curve lies $10,000 to the left of the private marginal benefit curve. B) marginal social cost curve lies $10,000 to the right of the private marginal benefit curve. C) marginal social benefit curve lies $10,000 below the private marginal benefit curve. D) marginal social benefit curve lies $10,000 above the private marginal benefit curve.
In the simple Keynesian model of the determination of income, planned investment is
A) an endogenous parameter. B) autonomous and thus an exogenous parameter. C) explained by the model of income determination. D) None of the above.
Suppose the market for good X has a four-firm concentration ratio of 0.70. Having worked for the four largest firms in the industry, you know the sales for these four firms are given by $200,000, $225,000, $250,000, and $275,000. Based on this information, we know that sales for the remaining firms in the industry are:
A. $407,143. B. $943,332. C. $687,500. D. $550,500.