In one day, Sue can change the oil on 20 cars or change the tires on 20 cars. In one day, Fred can change the oil on 20 cars or change the tires on 10 cars
Sue's opportunity cost of changing oil is ________ than Fred's and her opportunity cost for changing tires is ________ than Fred's. A) greater; less
B) less; greater
C) less; less
D) greater; greater
A
You might also like to view...
Explain what would happen to the equilibrium price and quantity of oranges if the supply of oranges increased while the demand for oranges decreased
What will be an ideal response?
If an unanticipated increase in aggregate demand results in an output beyond the economy's long-run capacity, long-run equilibrium will eventually be restored by
a. an increase in the economy's productive capacity (LRAS shifts to the right). b. higher resource prices, an increase in SRAS, and a decrease in the general level of prices. c. higher resource prices, a decrease in SRAS, and an increase in the general level of prices. d. a decrease in the natural rate of unemployment.
Competitive markets result in allocative efficiency because they
A. exhaust all possible benefits for the consumer. B. exhaust all possibilities for mutually beneficial trade. C. distribute resources in the most equitable way. D. generate all possible benefits for the consumers.
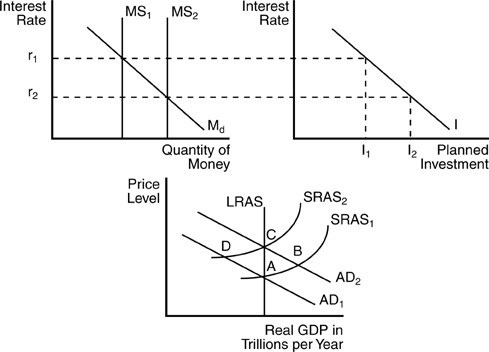 In the above figure, if the economy is initially at an equilibrium output at point A and the interest rate is r1, then an open market purchase of bonds by the Fed will
In the above figure, if the economy is initially at an equilibrium output at point A and the interest rate is r1, then an open market purchase of bonds by the Fed will
A. cause interest rates to increase and output to decline. B. cause interest rates to decline to r2, investment to increase to I2, and the AD curve to shift upward to the right. C. not have any impact on short- or long-run equilibrium real Gross Domestic Product (GDP). D. cause interest rates to decline to r2, investment to decline, and aggregate demand to shift inward to the left.