Identify and briefly describe the labeled structures of the long bone in this picture. 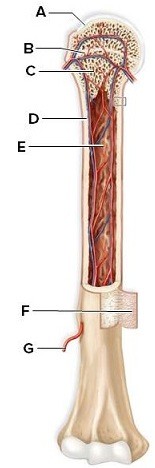 A: ________B: ________C: ________D: ________E: ________F: ________G: ________
A: ________B: ________C: ________D: ________E: ________F: ________G: ________
What will be an ideal response?
A: hyaline cartilage: found at the articular surface of bones
B: growth plate: area of cartilage between the primary ossification center and secondary ossification center which makes growth possible
C: spongy bone: may contain red bone marrow where blood cells are produced
D: compact bone: type of bone that consists of osteons consisting of concentric layers of matrix and osteocytes in lacunae
E: medullary cavity: central cavity of a long bone that contains yellow bone marrow for fat storage
F: periosteum: fibrous membrane that encases long bone
G: blood vessels: provide nutrients and oxygen to the bone
You might also like to view...
A type of transport of a solute across a membrane, up its concentration gradient, using protein carriers driven by the expenditure of chemical energy is known as
A. osmosis. B. diffusion. C. facilitated transport. D. active transport. E. exocytosis.
The sex hormones of many animals are a specific type of lipid molecule known as
a. fatty acid. b. phospholipid. c. carotenoid. d. steroid. e. lipoprotein.
The most common forms of color blindness result in the inability to properly perceive the colors
____________________ and ___________________Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
Gliding motility can be used to propel bacteria ________.
A. through liquids only B. along the framework of the cytoskeleton of host cells C. across solid substrates only D. through the air only