A hard disk has the following parameters:
• 6 surfaces
• 20K tracks per surface
• 256 sectors per track
• 512 bytes per sector
• rotational speed 7,200 rpm
a. What is the capacity of the drive?
b. What is the rotational latency?
c. Once a sector has been accessed, what is the rate at which data is read?
a. Capacity = sides × tracks/side × sectors/track × bytes/sector = 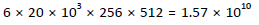 bytes
bytes
b. Rotational latency = 1/2 cycle. 7,200 rpm = 120 rps. One revolution = 8.33 ms. latency = 4.17 ms.
c. 512 × 8 bits are read in 8.33ms/256. Data rate = 4096/ 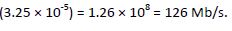
You might also like to view...
Explain the concept of "perceived usefulness" in the context of technology acceptance model (TAM).
What will be an ideal response?
An existing application stores sensitive information on a non-boot Amazon EBS data volume attached to an Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud instance. Which of the following approaches would protect the sensitive data on an Amazon EBS volume?
A. Upload your customer keys to AWS CloudHSM. Associate the Amazon EBS volume with AWS CloudHSM. Re-mount the Amazon EBS volume. B. Create and mount a new, encrypted Amazon EBS volume. Move the data to the new volume. Delete the oldAmazon EBS volume. C. Unmount the EBS volume. Toggle the encryption attribute to True. Re-mount the Amazon EBS volume. D. Snapshot the current Amazon EBS volume. Restore the snapshot to a new, encrypted Amazon EBS volume. Mount the Amazon EBS volume
List and describe the four main system changeover methods. Which one generally is the least expensive? Which is the safest? Explain your answers.
What will be an ideal response?
One assertion that locality is based on is that as a function of time, the probability that a given unit of memory is referenced tends to change __________.
A. slowly B. rapidly C. dramatically D. not at all