In an interference pattern, the wavelength and frequency are
a. the same in both the regions of constructive interference and the regions of destructive interference.
b. greater in regions of constructive interference than in regions of destructive interference.
c. smaller in regions of constructive interference than in regions of destructive interference.
d. unchanged in regions of destructive interference but greater in regions of constructive interference.
e. unchanged in regions of destructive interference but smaller in regions of constructive interference.
a
You might also like to view...
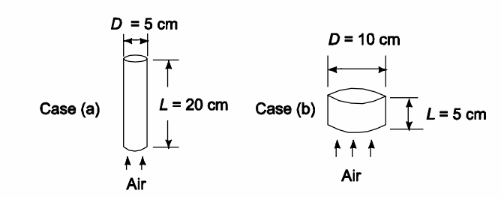
An automotive catalytic convertor is a packed bed in which a platinum catalyst is coated on the surface of small alumina spheres. A metal container holds the catalyst pellets and allows engine exhaust gases to flow through the bed of pellets. The catalyst must be heated by the exhaust gases to 300°C before the catalyst helps combust unburned hydrocarbons in the gases. The time required to achieve this temperature is critical because unburned hydrocarbons emitted by the vehicle during a cold start comprise a large fraction of the total emissions from the vehicle during an emission test. A fixed volume of catalyst is required but the shape of the bed can be modified to increase the heat-up rate. Compare the heat-up time for a bed 5-cm-diameter and 20-cm-long with one 10 cm diameter and
5-cm-long. The catalyst pellets are spherical, 5-mm-diameter, have a density of 2 g/cm3, thermal conductivity of 12 W/(m K) and specific heat of 1100 J/(kg K). The packed-bed void fraction is 0.5. Exhaust gas from the engine is at a temperature of 400°C, a flow rate of 6.4 gm/s, and has the properties of air.
GIVEN

FIND
The heat-up time (t) for the pellet surface temperature (Tp) to reach 300°C
ASSUMPTIONS
The initial temperature of the bed (To) = 20°C
SKETCH
Kirchhoff's voltage rule for a closed loop is an example of
A) conservation of energy. B) conservation of charge. C) conservation of momentum. D) conservation of force.
A block of mass m is pushed against a spring of spring constant k. The spring is compressed by a distance d, the block is then released. It is launched by the spring along a horizontal frictionless surface with a final speed v
A second block, this one having mass 4m is pushed against the same spring and released, gaining a final speed 2v. By what distance was the spring compressed in the second case? A) d B) 2d C) 4d D) 16d E) 25d
Imagine you are holding a long rope under tension attached to a distant support. You can generate periodic waves by shaking the end up and down. Changing which of the following will least affect the velocity of waves along the string?
A. Tension B. Frequency C. Mass per unit length of rope D. None of these choices affect the wave speed