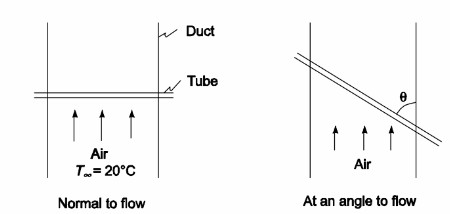
An engineer is designing a heating system that consists of multiple tubes placed in a duct carrying the air supply for a building. She decides to perform preliminary tests with a single copper tube, 2-cm-O.D., carrying condensing steam at 100°C. The air velocity in the duct is 5 m/s and its temperature is 20°C. The tube is placed normal to the flow, but it may be advantageous to place the tube at an angle to the air flow and thus increase the heat transfer surface area. It the duct width is 1 m, predict the outcome of the planned tests and estimate how the angle ? will affect the rate of heat transfer. Are there limits?
GIVEN
• A copper tube carrying condensed steam in an air duct
• Tube outside diameter (D) = 2 cm = 0.02 m
• Steam temperature (Ts) = 100°C
• Air velocity (U?) = 5 m/s
• Air temperature (T?) = 20°C
• Duct width (w) = 1 m
FIND
• Is it more advantageous to have the tubes normal to the air flow or at some angle to the air flow?
ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state
• Air velocity in the duct is uniform
• Thermal resistance due to steam condensing is negligible
• Thermal resistance of the tube wall is negligible
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0251 W/(m K) Kinematic viscosity
(?) = 15.7 × 10–6 m2/s Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71
The Reynolds number based on the tube diameter is
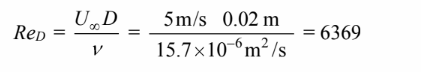
For the perpendicular position, the tube length (L) = w = 1 m and the Nusselt number can be calculated with ? = 90°
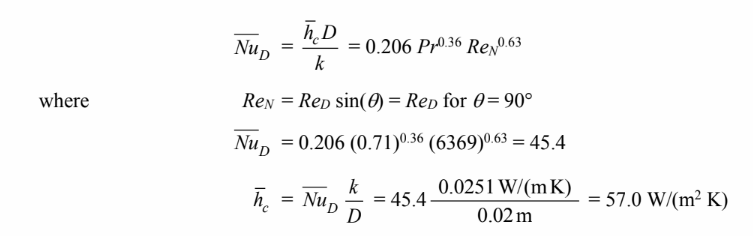
The rate of heat transfer is
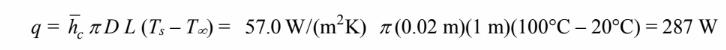
For the angled position, the tube length (L) = w/sin?.
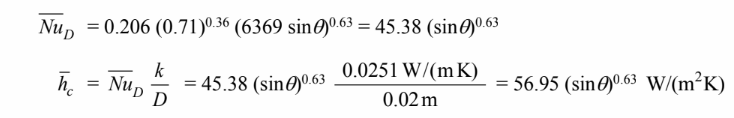
The rate of heat transfer is
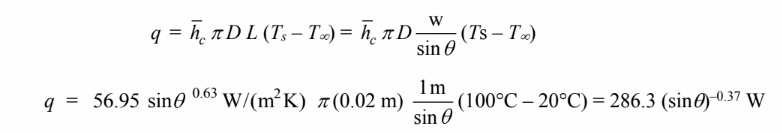
The engineer will find that the rate of heat transfer will increase because the heat transfer coefficient decreases with (sin?)0.63 but the area increases with 1/sin?. Therefore, the rate of heat transfer increases with 1/(sin?)0.37.
You might also like to view...
A pendulum that on Earth has period 0.52 s is taken to the surface of a large asteroid, where it is measured to have period 1.7 s. What is the value of the gravitational acceleration on the surface of that asteroid?
A. 5.78 
B. 0.48 
C. 3.0 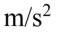
D. 0.92 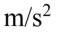
Newton's Second Law in 1 Dimension: In a certain particle accelerator, a proton reaches an acceleration of 9.0 × 1013 m/s2. The mass of a proton is 1.67 × 10-27 kg. What is the force on the proton?
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
The masses of Neptune and Uranus were first determined by:
A) observations of their motions around the Sun. B) observations of their magnetic fields. C) their densities divided by their volumes. D) observations of the motions of their satellites. E) their compositions.
The position x(t) of a particle as a function of time t is given by the equation x(t) = (3.5 m/s)t - (5.0 m/s2)t2. What is the average velocity of the particle between t = 0.30 s and t = 0.40 s?
What will be an ideal response?