Given that GDP is a measure of what is produced in a country, explain how the expenditure approach can measure GDP. How are items produced, but not yet sold, accounted for in the expenditure approach?
The expenditure approach measures GDP by summing the purchases of final goods and services by the four sectors of the economy. This is a reflection of production because an item can not be purchased unless it has been produced. Even items that have been produced, but not yet sold, are accounted for in the expenditure approach because national income accountants assume that anything that is produced but not sold to consumers is bought by the firm that produced it. These items would show up as part of the firms' inventory, and therefore would be counted as part of investment.
You might also like to view...
Everything else held constant, an increase in autonomous planned investment spending will cause the IS curve to shift to the ________ and aggregate demand will ________
A) right; increase B) right; decrease C) left; increase D) left; decrease
According to the rational expectations theory, expansionary monetary policy is fully effective only if
a. the policy is anticipated by workers and firms. b. aggregate supply shifts to the left. c. the economy is operating at or above its potential output level. d. policy makers follow through on their previously announced plans. e. the effects of the policy are unexpected.
In principle, we would expect the aggregate demand curve to be vertical because the price level is a reference point, the actual value of which should not matter.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Exhibit 4-2 Supply and demand curves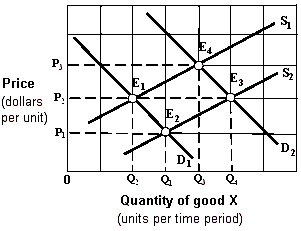
A. E1 to E2. B. E1 to E3. C. E4 to E1. D. E3 to E4.