Complementary goods
a. are usually used in conjunction with each other
b. are usually used in place of one another
c. do not adhere to the law of demand
d. are goods whose demand rises as incomes rise
e. are goods whose demand falls as wealth falls
A
You might also like to view...
Explain briefly the vent-for-surplus theory of international trade. What is the relevance of this theory to the current development experience of low-income economies?
What will be an ideal response?
For any constant returns production function, the isoquants for Q = 1, Q = 2, Q = 3, etc. will
A. be equally spaced, in that the distance between Q = 1 and Q = 2 is the same as Q = 2 and Q = 3, etc. B. all be inversely proportional to the inputs. C. be straight lines. D. exhibit diminishing returns in the long run.
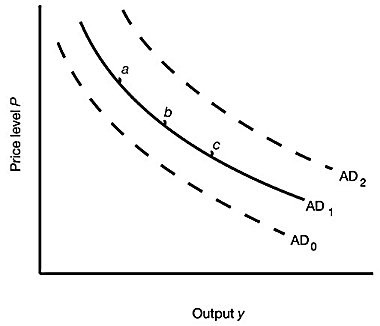
 Figure 14.1 shows three aggregate demand curves. A shift from curve AD1 to curve AD2 could be caused by a(n):
Figure 14.1 shows three aggregate demand curves. A shift from curve AD1 to curve AD2 could be caused by a(n):
A. decrease in the money supply. B. increase in taxes. C. decrease in the price level. D. increase in government spending.
When the demand curve for an input is a derived demand this means that
A. the law of diminishing marginal product does not hold. B. the demand curve slopes upward. C. the demand curve is derived from the demand for the final product being produced. D. the demand curve depends upon the MFC.