Using a carefully-labeled graph, explain the Life Cycle Hypothesis. What are some of the implications of the Life Cycle Hypothesis?
What will be an ideal response?
The Life Cycle Hypothesis is based on two main assumptions. First, an individual is assumed to work and earn income during the first period of their life. However, they do not have any earnings during the second period of their life. This is represented by the line labeled Earnings in the left-hand panel of Figure 10.3. In the figure, the individual is assumed to retire at age 65. The second major assumption of the Life Cycle Hypothesis is that individuals prefer stability in their consumption over their lifetimes. This is represented by the line labeled Consumption in the left-hand panel of Figure 10.3. The individual is able to smooth consumption by saving during the first stage of their lives, then drawing from those savings during the second period of life. This behavior is represented by the line labeled Saving in the right-hand panel of Figure 10.3.
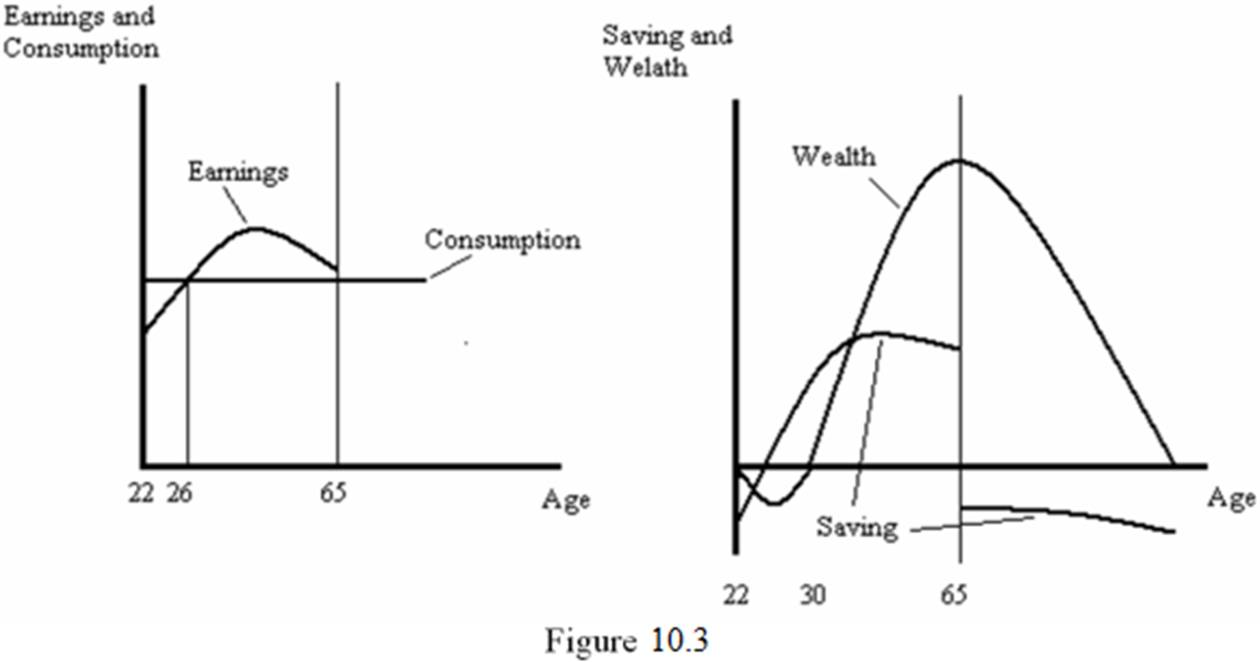
The Life Cycle Hypothesis helps us understand and predict how changes in the age-structure of a country's population will affect the rate of saving in that country. For example, countries in which the population is relatively young will have low rates of saving. Similarly, countries with aging populations will also have low savings rates.
You might also like to view...
The current account balance tabulates the value of a country's exports of goods and services minus the value of its imports of goods and services
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Which of the following is true about optimal search?
a. Optimal search occurs where the marginal benefit of search just equals the marginal cost of search, where the two curves intersect. b. Optimal search occurs when the total benefit of search exceeds the total cost of search. c. Optimal search occurs where the marginal benefit of search is equal to zero. d. Optimal search occurs when the marginal cost of search exceeds the marginal benefit of search.
Which of the following is considered human capital? Knowledge acquired from
a. early childhood education programs b. job training c. on-the-job experience d. All of the above are correct.
Refer to Figure 4.3. Which diagram most likely represents the indifference map for left shoes and right shoes?
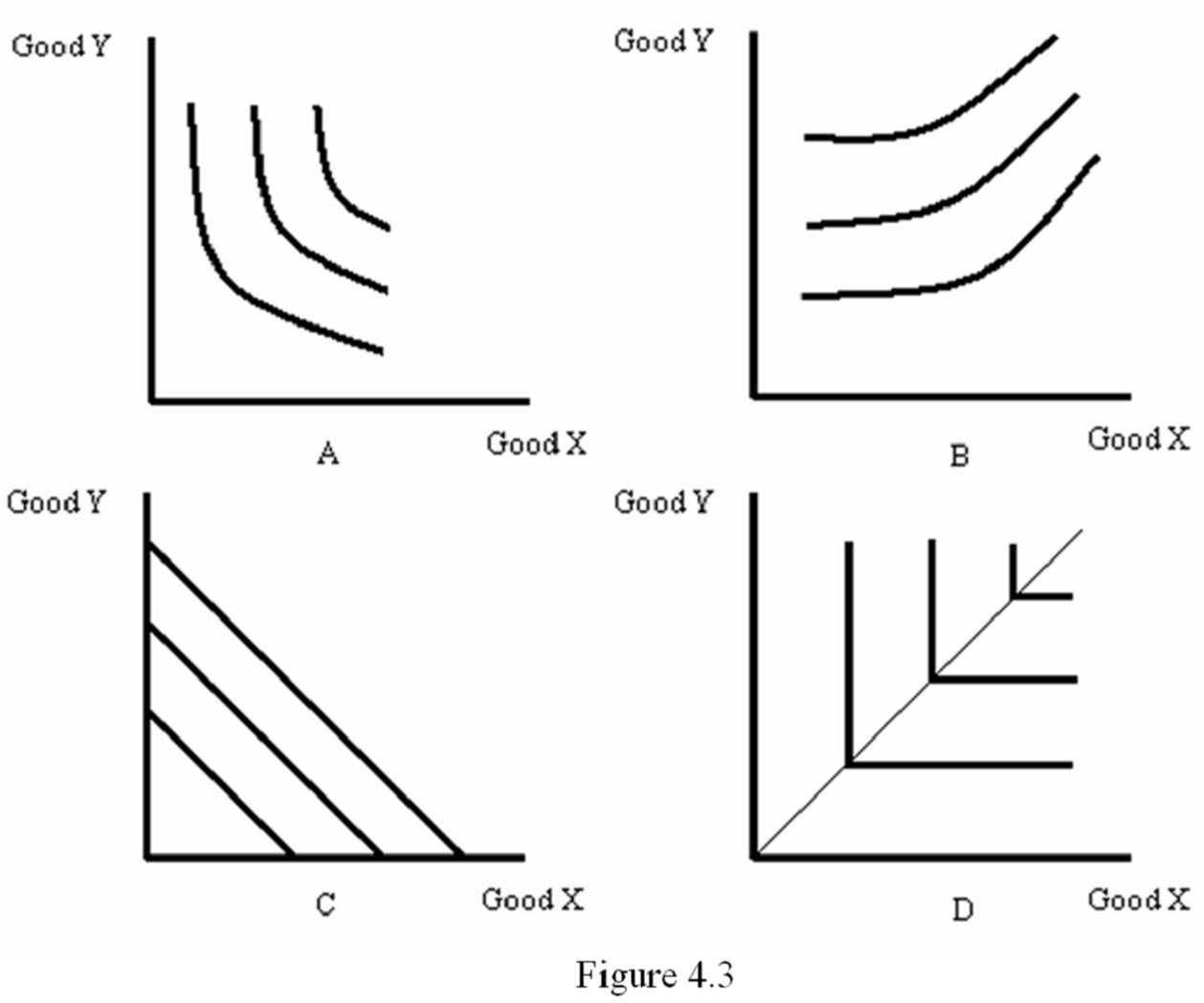
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D