At any point where a monopolist's marginal revenue is positive, the downward-sloping straight-line demand curve is:
A. perfectly elastic, as is the perfectly competitive firm's.
B. elastic but not perfectly elastic, and a perfectly competitive firm's demand curve is perfectly elastic.
C. elastic but not perfectly elastic, and a perfectly competitive firm's demand curve is perfectly inelastic.
D. inelastic, while a perfectly competitive firm's demand curve is perfectly elastic.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Ignoring any supply-side effects, to close a recessionary gap of $100 billion with a government expenditure multiplier of 5, the government could
A) increase government expenditure on goods and services by $100 billion. B) raise taxes by $100 billion. C) increase government expenditure on goods and services by $20 billion. D) raise taxes by more than $20 billion. E) decrease government expenditure on goods and services by $20 billion.
One of the timing problems with fiscal policy is an "operational lag" that occurs between the:
A. time the need for fiscal action is recognized and the time that action is actually taken. B. beginning of a recession and the time that it is recognized that the event is occurring. C. time that fiscal action has an impact on output, employment, and the price level and the time by which it can be determined if the policy is effective. D. time that fiscal action is taken and the time that action has an impact on output, employment, and the price level.
Our capital account balance in 2009 was a
A. surplus of about $500 billion. B. surplus of about $400 billion. C. deficit of about $500 billion. D. deficit of about $700 billion.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 5.2 below to answer the question(s) that follow.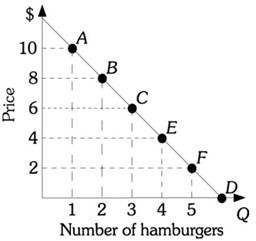 ?Figure 5.2Refer to Figure 5.2. If the price of a hamburger increases from $8 to $10, the price elasticity of demand equals ________. Use the midpoint formula.
?Figure 5.2Refer to Figure 5.2. If the price of a hamburger increases from $8 to $10, the price elasticity of demand equals ________. Use the midpoint formula.
A. -0.33 B. -3.0 C. -30. D. -300