In long-run equilibrium, a monopolistically competitive firm achieves optimal productive efficiency but not optimal allocative efficiency.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
False
You might also like to view...
The marginal cost of serving an additional user of a public good is zero.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
This graph reflects a Keynesian viewpoint. How would the economy respond to an aggregate demand decrease under the classical model?
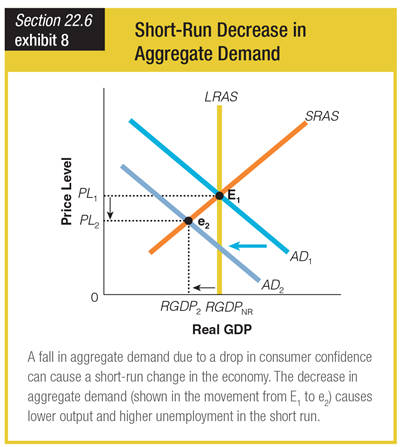
a. The shift from AD1 to AD2 would also shift LRAS leftward to a new position at RGDP2.
b. The economy would quickly adjust to a new point of long-run equilibrium where AD2 intercepts LRAS.
c. The shift from AD1 to AD2 would produce a short-run equilibrium point at e2 that differs from E1.
d. The economy would quickly adjust to a new point of long-run equilibrium where AD1 intercepts LRAS.
The individual quantity demanded is the amount that the buyer is allowed to purchase at a given price.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Which of the following is an example of an intermediate good?
A. the chocolate chips you purchase to make cookies to sell at a bake sale for your kids' school B. the lumber you buy to build a house for your dog C. the blueberries you buy to bake yourself some muffins D. the tortillas you buy to make yourself a burrito for lunch