Which theory best explains the wealth inequalities amongst nations?
A) weather
B) government institutions
C) natural selection
D) factors outside of any human control
E) levels of corruption
B
You might also like to view...
In the monetary small open-economy model with a flexible exchange rate, an increase in the foreign price level decreases
A) domestic output, but has no effect on the domestic price level or the nominal exchange rate. B) the domestic price level, but has no effect on domestic output or the nominal exchange rate. C) the nominal exchange rate, but has no effect on domestic output or the domestic price level. D) the domestic price level and the nominal exchange rate, but has no effect on domestic output.
Cooperation that continues as long as the players continue to cooperate is
A) a zero-sum game. B) a negative-sum game. C) tit-for-tat strategic behavior. D) opportunistic behavior.
the multiplier is the ratio of the change in real GDP to the change in autonomous expenditure
a. true b. false
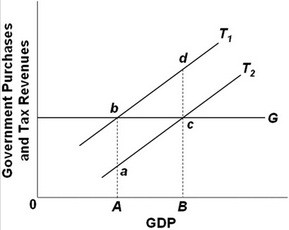 Refer to the above diagram. Assume that G and T1 are the relevant curves, the economy is currently at A, and the full-employment GDP is B. This economy has:
Refer to the above diagram. Assume that G and T1 are the relevant curves, the economy is currently at A, and the full-employment GDP is B. This economy has:
A. neither a surplus nor deficit in the actual budget. B. a cyclically adjusted budget deficit. C. an actual budget deficit. D. an actual budget surplus.