If an electron is accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 300 V, find its approximate speed at the end of this process. (e = 1.6 × 10^-19 C; me = 9.1 × 10^-31 kg)
a. 2.5 × 10^7 m/s
c. 1.0 × 10^7 m/s
b. 2.1 × 10^7 m/s
d. 1.4 × 10^7 m/s
C
You might also like to view...
Specific Heat: A glass beaker of unknown mass contains 74.0 ml of water. The system absorbs 2000.0 cal of heat and the temperature rises 20.0°C as a result. What is the mass of the beaker? The specific heat of glass is 0.18 cal/g ? °C, and that of water is 1.0 cal/g ? C°.
A. 140 g B. 560 g C. 540 g D. 270,000 g
In a situation where an object can move only along the x axis, a book states “the force on the object is F = -kx, where k is a constant, and x is the object’s position coordinate.” Is F being used here as a shorthand symbol for 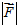 (A) or Fx (C)?
(A) or Fx (C)?
A. A B. C
A system of blocks and a frictionless pulley is shown in the figure. Block A has a mass of 2.0 kg and is on a rough horizontal surface for which ?s = 0.40 between the surface and block A
The rope pulls horizontally on block A. Block C has a mass of 1.0 kg. An external force P = 23.0 N, applied vertically to block A, maintains the system at rest as shown in the figure. What is the friction force on block A? A) 6.3 N B) 6.9 N C) 7.5 N D) 5.7 N E) 5.1 N
Air pressure is 1.0 × 10^5 N/m2, air density is 1.3 kg/m3, and the density of soft drinks is 1.0 × 10^3 kg/m3 . If one blows carefully across the top of a straw sticking up 0.080 m from the liquid in a soft drink can, it is possible to make the soft drink rise half way up the straw and stay there. How fast must the air be blown across the top of the straw?
a. 76 m/s c. 25 m/s b. 27 m/s d. 0.99 m/s