Which of the following is a key diagnostic indicator of infection with Mycobacterium leprae?
A) blister-like lesions
B) a distinctive red rash that lasts for days
C) pus-filled abscesses
D) localized loss of the sense of touch
E) severe inflammation with swelling
D
You might also like to view...
The amino acids of the protein keratin are arranged predominantly in an ?-helix. This secondary structure is stabilized by _____
A) covalent bonds B) peptide bonds C) ionic bonds D) polar bonds E) hydrogen bonds
When one gene is able to modify the effect of a second gene, the phenomenon is known as:
A. simple dominance B. epistasis C. recessiveness D. independent assortment E. segregation
The accompanying figures are representative of which of the following?
a. Anthophyta
b. Gnetophyta
c. Ginkophyta
d. Cycadophyta
e. Coniferophyta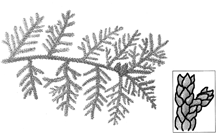
A student uses restriction enzymes to cut a DNA molecule into fragments. The digested DNA is loaded into the wells of an agarose gel and the gel is subjected to an electric current. Upon completion of the run, the gel is stained. The rate of migration of the DNA fragments through the agarose gel is determined by the
(A) ratio of adenine to cytosine in the fragment (B) presence of hydrogen bonds between base pairs (C) length of time the electrophoresis unit is allowed to operate (D) number of nucleotides in the fragment (E) volume of the starting sample