The determinants of aggregate demand:
A. explain why the aggregate demand curve is downsloping.
B. explain shifts in the aggregate demand curve.
C. demonstrate why real output and the price level are inversely related.
D. include input prices and resource productivity.
B. explain shifts in the aggregate demand curve.
You might also like to view...
An economist claims that any point not on a production possibilities frontier cannot be best. What is his reasoning to support this?
A. A point inside the frontier implies that society is not facing up to the problem of scarcity. B. A point inside the frontier limits growth, and growth is always a goal worth pursuing. C. A point inside the frontier represents inflation, and inflation is a dangerous situation. D. A point inside the frontier results in fewer goods, and more is always better. E. A point inside the frontier is inefficient and represents wasted resources.
Scott used $4,000,000 from his savings account that paid an annual interest of 5% to purchase a hardware store. After one year, Scott sold the business for $4,100,000 . His accounting profits is:
a. $300,000 b. $100,000 c. $80,000 d. $20,000
In 1974, one could buy a theater ticket for $1.25 . Today the same theater ticket costs $6.50 . Which pair of CPIs would imply that the cost in today's dollars was the same for both tickets?
a. 60 in 1964 and 390 today b. 75 in 1964 and 390 today c. 80 in 1964 and 404 today d. 95 in 1964 and 475 today
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, a decrease in government spending that decreases aggregate demand from AD1 to AD will lead to a short-run equilibrium at__ creating _____gap.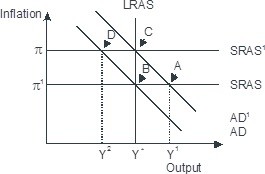
A. B; no output B. D; an expansionary C. B; recessionary D. D; a recessionary