Suppose the government expenditure increases by $200 and the simple spending multiplier equals 5 . The final increase in output will be:
a. $6000
b. $500.
c. $200.
d. more than $200.
e. less than $200.
d
You might also like to view...
Use the following graphs to answer the next question.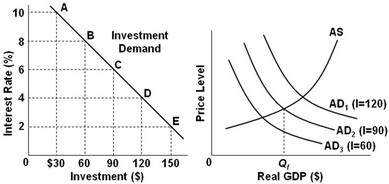 In the graphs, the numbers in parentheses near the AD1, AD2, and AD3 labels indicate the level of investment spending associated with each curve, respectively. All numbers are in billions of dollars. The interest rate and the level of investment spending in the economy are at point B on the investment demand curve. To achieve the long-run goal of a noninflationary, full-employment output of Qf in the economy, the Fed should ________.
In the graphs, the numbers in parentheses near the AD1, AD2, and AD3 labels indicate the level of investment spending associated with each curve, respectively. All numbers are in billions of dollars. The interest rate and the level of investment spending in the economy are at point B on the investment demand curve. To achieve the long-run goal of a noninflationary, full-employment output of Qf in the economy, the Fed should ________.
A. increase investment spending from $30 billion to $60 billion B. decrease the interest rate from 8% to 6% C. decrease the interest rate from 10% to 8% D. decrease the interest rate from 6% to 4%
Use the firm's long-run cost-minimizing decision rule to explain the differences in the relative use of capital and labor in agriculture in the United States and the Peoples Republic of China
What will be an ideal response?
Which of the following statements is correct?
a. The classical aggregate AD curve can be shifted by monetary and non-monetary factors. b. The classical AS schedule is horizontal while the Keynesian aggregate AS schedule is vertical. c. The Keynesian AD curve only shifts in response to monetary factors. d. The classical aggregate supply schedule slopes upward to the right while the Keynesian aggregate supply schedule is vertical. e. none of the above are correct.
The law of diminishing marginal utility states that as we consume increasing amounts of a good or service, _________________________.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).