A decrease in price level will
A) shift the planned expenditures curve upward.
B) cause a movement up along the planned expenditures curve.
C) shift the planned expenditures curve downward.
D) cause a movement down along the planned expenditures curve.
A
You might also like to view...
A cash-payment welfare program, where eligibility is no longer an entitlement but emphasizes welfare-to-work is
a. food stamps b. Medicare c. Social Security d. TANF e. SSI
Under the Term Auction Facility (TAF), the rate that a depository institution pays on a loan from the Fed is determined by
a. the federal funds rate. b. the discount rate. c. the real rate of interest. d. a bidding process allocating the funds to those willing to pay the highest rates.
Suppose an event occurs that causes people to gain faith in the ability of Europeans to pay their euro-denominated debt. Suppose that before this happens the exchange rate between the euro and the dollar is .75 euros/dollar. The resulting exchange rate would likely
A. cause the exchange rate to have to be expressed in dollars per euro (because the other way would no longer make sense). B. rise to (perhaps) .9 euros/dollar. C. fall to (perhaps) .6 euros/dollar. D. remain unchanged.
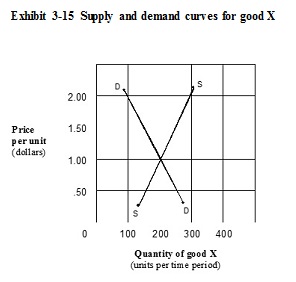
A. no change, because an equilibrium already exists. B. the price to fall below $.50 and both the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded to rise. C. the price to remain the same, but the supply curve to shift to the left. D. the price to rise above $.50, the quantity supplied to rise, and the quantity demanded to fall.