In the long run, what happens to the demand curve facing a monopolistically competitive firm that is earning short-run profits?
A) The demand curve will shift to the left and became more elastic.
B) The demand curve will shift to the left and became less elastic.
C) The demand curve will shift to the right and became more elastic.
D) The demand curve will shift to the right and became less elastic.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
The velocity of circulation is equal to
A) the price level multiplied by the quantity of money. B) nominal GDP divided by the quantity of money. C) the quantity of money divided by the price level and then multiplied by real GDP. D) the quantity of money divided by nominal GDP. E) the price level divided by real GDP.
Which of the following is the term used when average costs go down as the measure of output goes up?
a. Relative advantage b. Absolute advantage c. Comparative advantage d. Economies of scale
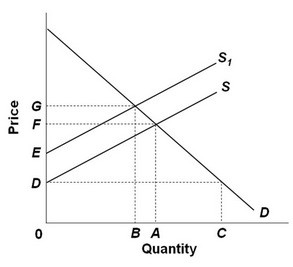 Refer to the above supply and demand graph. In the graph, point A is the current equilibrium level of output of this product and point B is the optimal level of output from society's perspective. S is the supply curve without a tax and St is the supply curve with a tax. If government corrects this externality problem with a tax so that all the costs are included in the cost of production, then the product price will be set at point:
Refer to the above supply and demand graph. In the graph, point A is the current equilibrium level of output of this product and point B is the optimal level of output from society's perspective. S is the supply curve without a tax and St is the supply curve with a tax. If government corrects this externality problem with a tax so that all the costs are included in the cost of production, then the product price will be set at point:
A. E. B. D. C. F. D. G.
The ability of the DVCs to use the technologies of the IACs is somewhat limited because:
A. the IACs have patents on most of their technologies. B. the IACs and the DVCs have much different resource endowments. C. the technologies of the IACs rely heavily on unskilled labor. D. IAC technologies are labor-intensive, while DVC technologies are capital-intensive.