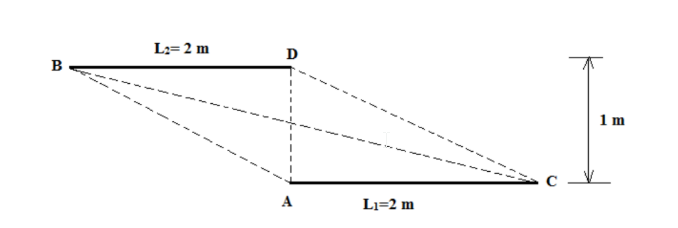
Two parallel plates of infinite extent perpendicular to the page are situated relative to each other as shown in the figure. The upper plate is at 300°C and the lower plate is at 100°C. Determine the net rate of radiation heat transfer from the upper and lower plate assuming the environment is at a temperature below 100°C. Assume that both the lower surface of the upper plate and the upper surface of the lower plate are black.
GIVEN
• Two parallel plates of infinite extent perpendicular to the page.
• Upper plate temperature (T2) = 3000C
• Lower plate temperature (T1)= 1000C
• Length of the plates L1 = L2 = 2 m
• Distance between the plates (R) = 1 m
FIND
(a) Net rate of radiation heat transfer from upper and lower plate.
ASSUMPTIONS
• Lower surface of upper plate and upper surface of lower plate are black.
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
The Stephan-Boltzmann constant (?) = 5.67 × 10–8 W/(m2 K4)
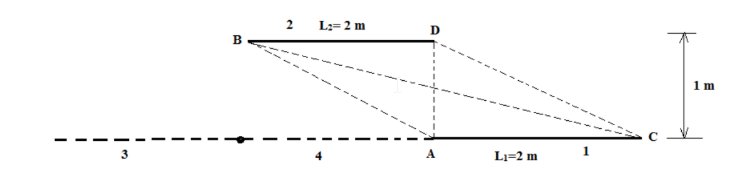
Two imaginary plates 3 and 4 are extended along the plate 1 so that the center of both upper and lower plates align.
By symmetry F21 = F23
Thus, F21= 0.5*(F2(1,4,3)- F24 )
Now, for plates of infinite extent perpendicular to the plane and of given dimensions y=6 m D=1
m y/D= 6 width of plates (x)= ?, x/D=?
Shape factor for directly opposed plane F2(1,3,4)= 0.88
For plates 2 and 4, the shape factor F24 is calculated as y=2 m D=1 m y/D= 2 width of plates (x)= ?, x/D=?
Shape factor for directly opposed plane F24= 0.65 Thus, the shape factor F21 is calculated as
F21= 0.5*(0.88- 0.65 ) = 0.115 Thus, net radiative heat transfer between upper and lower plates is Q/A2 = 4 4
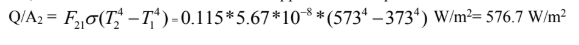
You might also like to view...
The Large Hadron Collider is expected to produce protons with kinetic energy 7 TeV. What is the speed of these protons?
A) less than 0.9000 c B) 0.9500 c C) 0.9990 c D) greater than 0.9999 c E) 0.9000 c
A solid cylinder (I = MR2/2) has a string wrapped around it many times. When I release the cylinder, holding on to the string, the cylinder falls and spins as the string unwinds. What is the downward acceleration of the cylinder as it falls?
a. 0 c. 6.5 m/s2 b. 4.9 m/s2 d. 9.8 m/s2
How would you reduce fouling in a compact heat exchanger?
What will be an ideal response?
Which of these situations is possible?
1.Energy is transferred by heat to a system and the internal energy of the system decreases. 2.Energy is transferred by heat to a system and the internal energy of the system remains constant. 3.Energy is transferred by heat to a system and the internal energy of the system increases. 4.All of these are possible.