A neutron star is
A) the remains of a star that died in a massive star supernova (if no black hole was created).
B) the remains of a star that died by expelling its outer layers in a planetary nebula.
C) a star made mostly of elements with high atomic mass numbers, so that they have lots of neutrons.
D) an object that will ultimately become a black hole.
A) the remains of a star that died in a massive star supernova (if no black hole was created).
You might also like to view...
An interstellar gas cloud has the mass to form hundreds of stars. What generally happens to it?
What will be an ideal response?
Name three differences between terrestrials and jovian planets
What will be an ideal response?
As shown below, a square loop of wire of side a moves through a uniform magnetic field of magnitude B perpendicular to the page at constant velocity 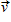

src="https://sciemce.com/media/2/ppg__cognero__Chapter_32_Faraday_apos_s_Law_of_Induction.__media__9a07393c-567d-4f49-9f99-3f5a45c9773c.PNG" style="vertical-align:-3px;" width="20px" height="19px" />
. Which one, if either, is correct, and why?
?
?
B.
C.
 .
.D.
 .
.E.
A compound microscope consists of an objective lens of focal length f0 and an eyepiece that by itself produces an angular magnification 25.0
The microscope is designed so that the object to be viewed is on the left side of the objective lens and is focused in a plane that is 28.00 cm away from the right-hand (or inside) focal point of the objective lens. When properly adjusted, the eyepiece and the objective lens are 29.90 cm apart. The eyepiece magnification is based on an image at infinity and a near point at 25.0 cm. What is f0?