Refer to the information provided in Figure 6.15 below to answer the question that follows.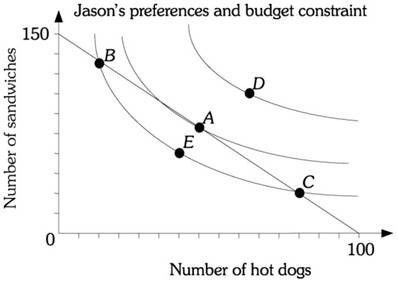 Figure 6.15Refer to Figure 6.15. Why is Jason not maximizing his utility at point B?
Figure 6.15Refer to Figure 6.15. Why is Jason not maximizing his utility at point B?
A. His marginal utility per dollar spent on the last sandwich is less than his marginal utility per dollar spent on his last hot dog.
B. He is not spending his entire budget.
C. His marginal utility per dollar spent on the last sandwich is greater than his marginal utility per dollar spent on his last hot dog.
D. He is maximizing his utility at point B.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Suppose you lend $5,000 to your brother for one year at a nominal interest rate of 7%. Inflation during that year is 4%. As a result, you will receive ________ at the end of the year
A) $5,150 B) $5,225 C) $5,350 D) $5,550
If a firm buys a specialized metal stamping machine that will last 4 years for $125,000 and cannot resell it, the sunk cost is
A) $0. B) $31,250. C) $125,000. D) $93,750.
Compared to a perfectly competitive industry, a monopolist with the same marginal cost and demand curve will charge:
a. a higher price and produce a higher volume of output. b. a lower price and produce a higher volume of output. c. a lower price and produce a lower volume of output. d. a higher price and produce a lower volume of output. e. the same price and produce the same volume of output.
The idea that if governments cut taxes but not spending, people will not change their behavior, and expansionary policy will have little expansionary effect is known as:
A. Keynesian policy. B. Ricardian equivalence. C. the invisible hand. D. Stimulus policy.