What is the key idea of classical growth theory that leads to the dismal outcome?
What will be an ideal response?
The "dismal outcome" in classical theory is the conclusion that in the long run real GDP per person equals the subsistence level. In classical growth theory, an increase in real GDP per person causes population increases that return real GDP per person to the subsistence level. In the classical growth theory, an increase in income creates a population boom. The increase in population increases the supply of labor. Because of diminishing returns to labor, the increase in the supply of labor lowers the real wage rate and people's incomes. Eventually the real wage rate falls to equal the subsistence level, at which time the population stops growing.
You might also like to view...
A shoe retailer does not give a bill for shoes purchased from his store and does not report his income correctly to evade taxes. If you pay him $50, ________
A) the GDP of your country will fall B) the GDP of your country will increase C) the trade surplus of your country will increase D) the GDP of your country will remain unchanged
What is the expenditure approach to measuring GDP?
What will be an ideal response?
For a monopolist with a linear demand curve, total revenue is maximum when:
a. marginal revenue is positive. b. marginal revenue is at its maximum. c. the price elasticity of demand is greater than unity. d. the price elasticity of demand is equal to unity. e. marginal revenue is at its minimum.
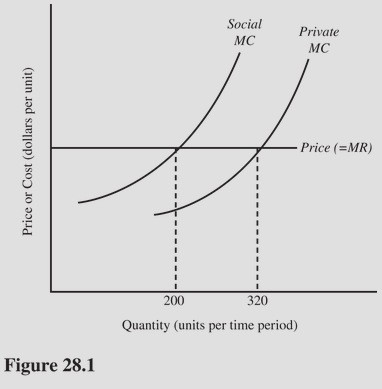 In Figure 28.1, if pollution costs are external, the rate of output will be
In Figure 28.1, if pollution costs are external, the rate of output will be
A. Greater than 320 units. B. Less than 200 units. C. 200 units. D. 320 units.