According to dynamic tax analysis, continually increasing the tax rate will eventually
A) cause an increase in the tax base.
B) have no impact on the tax base.
C) cause a decrease in the tax base.
D) result in an initial decrease in the tax base followed ultimately by a rise in the tax base.
C
You might also like to view...
Use the following diagram of the market for money to answer the next question.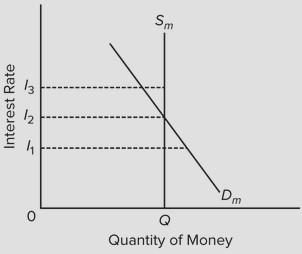 The downward slope of the money demand curve Dm is best explained in terms of the
The downward slope of the money demand curve Dm is best explained in terms of the
A. asset demand for money. B. wealth or real-balances effect. C. direct or positive relationship between bond prices and interest rates. D. transactions demand for money.
How is it logically possible for a monopolist to get different consumers to purchase different bundles on a menu (such as different sizes of coffee cups), and thereby achieve a form of price discrimination, even if the firm cannot observe the consumers' valuations directly? a. Different types of consumers have different tradeoffs between money and amounts of the good. b. The monopolist can use
a market-separation strategy. c. Social norms are powerful deterrents to lying about one's type. d. This is impossible: if one bundle is preferred by one type, logically it will be preferred by all.
If a binding price ceiling is imposed on the baby formula market, then
a. the quantity of baby formula demanded will increase. b. the quantity of baby formula supplied will decrease. c. a shortage of baby formula will develop. d. All of the above are correct.
Which of the following explains why a firm would be interested in knowing the price elasticity of demand for a good it sells?
A) The price elasticity of demand can be used to determine the impact of changes in income on quantity sold. B) Knowing the price elasticity of demand allows the firm to determine how the cost of producing additional units of the good will change. C) Knowing the price elasticity of demand allows the firm to calculate how changes in the price of the good will affect the firm's total profit. D) The price elasticity of demand allows the firm to calculate how changes in the price of the good will affect the firm's total revenue.