Exhibit 4-10 Supply and demand data for apricots
Bushels demandedper month
Price perbushel
Bushels suppliedper month
50
$5
80
55
4
75
60
3
70
65
2
65
70
1
55
In Exhibit 4-10, assume that the government initially sets a price floor of $4 for apricots, and then removes the $4 price floor. What effect will this price change have?
A. The price of apricots will rise.
B. The quantity of apricots demanded will fall.
C. The quantity of apricots supplied will decline.
D. Quantity supplied will continue to exceed quantity demanded.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Which of the following statements draws a false conclusion?
a. Life expectancy in an average African country is lower than in an average European country; therefore Europeans can expect to outlive Africans. b. Nations that currently produce no capital goods, and whose inhabitants are hungry, risk famine with internally funded capital investments. c. Some African nations have substantially more food and capital investment than others; therefore, their standard of living is higher. d. Population reduction policies, if effective, can improve the nation's wealth by increasing real per capita GDP. e. The vicious circle of poverty argument states that poverty precludes capital investment and that no capital investment perpetuates poverty.
The estimated demand for a good is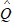 = 4800 - 16P - 0.65M - 1.5PRwhere Q is the quantity demanded of the good, P is the price of the good, M is income, and PR is the price of related good R. The good is
= 4800 - 16P - 0.65M - 1.5PRwhere Q is the quantity demanded of the good, P is the price of the good, M is income, and PR is the price of related good R. The good is
A. an inferior good since the coefficient on M is negative. B. a normal good since the coefficient on M is greater than one (in absolute value). C. a normal good since the coefficient on PR is negative. D. an inferior good since the coefficient on PR is negative. E. none of the above
Why does the Dow Jones Industrial Average have a value over 15,000 when the 30 stocks that make up the index all have values less than $200 per share?
What will be an ideal response?
Economic growth in the U.S. since 1950 has been characterized by:
A. An average growth rate in real GDP that is slower than the growth rate of the population B. A quadrupling of real GDP from 1950 to 2012 C. An average growth rate in real GDP that is faster than the growth rate of the population D. An average growth rate in real GDP per capita of about 6% per year