Comparative advantage is defined as
A) producing all goods at lower opportunity costs than other countries can.
B) producing more output of all goods than anyone else can.
C) producing one good at a lower opportunity cost than another country can.
D) the ability to produce more output from given inputs than anyone else can.
C
You might also like to view...
When there is an expansionary gap, inflation will ________, in response to which the Federal Reserve will ________ real interest rates, and output will ________.
A. decline; lower; expand B. increase; raise; decline C. decline; lower; decline D. decline; raise; decline
If real GDP grows by 3 percent, the velocity of circulation grows by 4 percent, and the quantity of money grows by 3 percent, then in the long run the inflation rate is
A) 0 percent. B) 7 percent. C) 10 percent. D) 4 percent. E) -4 percent.
According to the random walk theory of stock market? pricing,
A. if the price went up today it will probably go up tomorrow. B. people with economic training can make certain profits in the stock market. C. there are no predictable trends in stock prices. D. on any given? day, fifty percent of the stocks will increase in price and fifty percent will decrease in price.
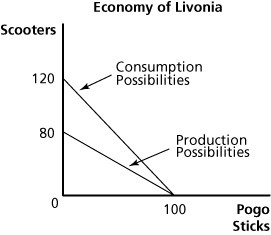 Figure 18.3Refer to Figure 18.3. The opportunity cost of producing scooters in Livonia is:
Figure 18.3Refer to Figure 18.3. The opportunity cost of producing scooters in Livonia is:
A. 2/3 of a pogo stick. B. 6/5 of a pogo stick. C. 1.5 pogo sticks. D. 1.25 pogo sticks.