Give a hypothetical example of a company that uses physical differences, prestige, location, and service to differentiate its product.
What will be an ideal response?
Examples will vary, but should show a thorough understanding of how physical differences, prestige, location, and service can be used for product differentiation. For example, a person named Lynn opens an Italian restaurant. She uses physical differences for product differentiation by the way the establishment is decorated, such as having an outdoor patio. Also, Lynn uses prestige by garnering several four-star reviews in magazine and newspapers. The location is near a shopping center, which doesn’t have an upscale Italian restaurant, so that makes Lynn’s restaurant stand out. Finally, she thoroughly trains the wait staff to make sure their service is efficient, non-obtrusive, and friendly.
You might also like to view...
Sharon purchases two products, X and Y, with a given fixed budget. The marginal utility she receives from the last unit of X she consumes is 60 utils, and the marginal utility she receives from the last unit of Y she consumes is 30 utils. The price of X is $2.00, and the price of Y is $1.00. Based on the equal marginal principle, these data suggest that Sharon
A. should buy more Y and less X. B. should buy less Y and X. C. should buy more X and less Y. D. is maximizing her total utility from the given fixed budget.
An increase in the real rate of interest that can be earned on U.S. investments above the rate that can be earned on investments in India would:
a. increase the price of the dollar in Indian rupees. b. increase the supply of dollars by those holding U.S. dollars. c. decrease the equilibrium exchange rate of Indian rupees per dollar. d. all of these.
The dominant Keynesian view of the 1960s and 1970s stressed that
What will be an ideal response?
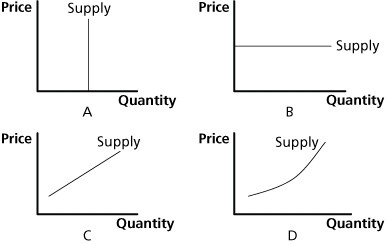 Figure 5.4In Figure 5.4, supply elasticity is zero in graph:
Figure 5.4In Figure 5.4, supply elasticity is zero in graph:
A. A. B. B. C. C. D. D.