Debate over the use of DDT to control malaria is likely to continue. However, over the past several decades, much has been learned about how this insecticide works, and why its extensive use poses an environmental concern
Discuss three characteristics of this chemical that cause it to be problematic.
DDT is a synthetic chemical, developed in the mid-1940s as an insecticide to be used against malaria. This chemical has many of the critical characteristics that cause it to be particularly harmful to a wide array of warm-blooded organisms, including humans. Its persistence, transport in the environment, and uptake by many non-target organisms contribute significantly to its environmental health concerns. DDT is not easily broken down in the environment, and even its by-products are toxic. DDT's environmental persistence is estimated to vary between 30 and 100 years. Because it is sprayed over wide areas, it easily gets into water supplies and affects aquatic food webs. Because it is taken up by insects and other small organisms found in lower trophic levels, its ability to bioaccumulate in higher organisms in the food chain is dependent on its fat solubility characteristic. That is, DDT is able to be stored in the tissues of living organisms without breaking down, and this characteristic leads to its biomagnification in the food web. Organisms that feed on other organisms whose tissues have stored DDT, are likely to store an even higher concentration. Some of the most well-documented environmental effects of DDT have been egg-shell thinning in birds of prey; however, cancer and developmental abnormalities have also been documented in amphibians and other higher vertebrates.
You might also like to view...
The copolymer styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), shown below, is used for making tires as well as bubble gum. Is it an addition polymer or a condensation polymer?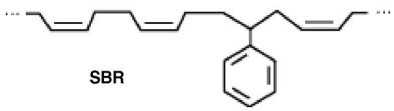
A. SBR is both an addition and a condensation polymer. B. SBR is an condensation polymer. C. SBR is neither an addition nor a condensation polymer. D. SBR is an addition polymer.
The following diagram illustrates the Rock Cycle.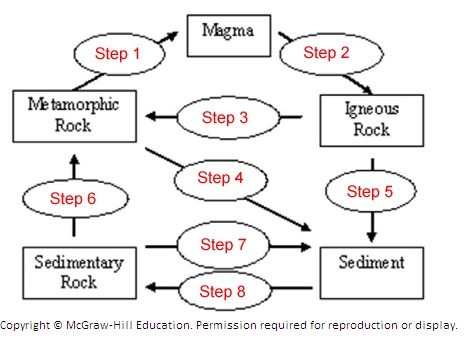 The diagram illustrates the Rock Cycle. Match the item below to step number 2 on the diagram.
The diagram illustrates the Rock Cycle. Match the item below to step number 2 on the diagram.
A. Cementation and compaction (lithification) B. Heat and pressure C. Weathering, transportation, deposition D. Cooling and solidification E. Melting
How long does it take to decompose:
Banana Peel Aluminum can Cardboard Plastic container
Why is stratospheric ozone loss a concern?
A) Stratospheric ozone is a major greenhouse gas; its loss will contribute to the cooling of the planet. B) Stratospheric ozone absorbs harmful ultraviolet radiation (UVB and UVC). C) Stratospheric ozone is a component of photochemical smog. D) Stratospheric ozone contributes to the brilliant auroras.