Urbanization is measured by:
A) the ratio of the population living in urban areas to the ratio of the people living in rural areas in a country.
B) the fraction of the population living in towns with a population of more than 5,000.
C) the fraction of the population living in towns with a population of more than 1,000.
D) the ratio of the population living in rural areas to the ratio of the people living in urban areas in a country.
B
You might also like to view...
The Laffer curve illustrates that
A) high tax rates could lead to lower tax revenues if economic activity is severely discouraged. B) lowering tax rates will always decrease tax revenues. C) lowering tax rates will always increase tax revenues. D) high tax rates would increase tax revenue and increase the labor supply as people work harder to maintain their standard of living.
Jamal maximizes utility by allocating his time among leisure, market work, and household work so that
a. expected marginal utility is equal among all three b. expected total utility per hour is equal among all three c. expected marginal utility per hour is equal among all three d. the maximum amount of goods and services can be acquired e. expected total utility of each use is equal
Answer the following statement(s) true (T) or false (F)
1. The long-run equilibrium level is where the economy will settle when undisturbed. 2. Changes in the stock of capital will alter the amount of goods and services the economy can produce. 3. In recent history, computers and specialized software shifted the short-run aggregate supply curve leftward. 4. Japan’s aging workforce has shifted that nation’s long-run aggregate supply curve rightward. 5. The short-run equilibrium level of real output and the price level are given by the intersection of the aggregate demand curve and the short-run aggregate supply curve.
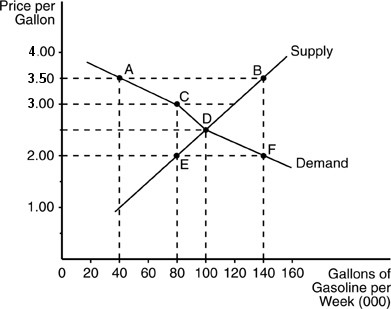 Refer to the above figure. At a price of $2 per gallon, the quantity demanded of gasoline is
Refer to the above figure. At a price of $2 per gallon, the quantity demanded of gasoline is
A. 100,000 gallons per week. B. 140,000 gallons per week. C. 60,000 gallons per week. D. 80,000 gallons per week.