Suppose that the average equilibrium monthly rental price of apartments and rooms in a college town had been steady at $600, but then the college expanded enrollment from 10,000 to 12,000, and suddenly there was a shortage of rental housing at the prevailing price of $600 . Which of the following is most likely to be true?
a. The shortage occurred because demand increased, and a new market equilibrium will feature higher rental prices and more rental units available on the market.
b. The shortage occurred because demand decreased, and a new market equilibrium will feature lower rental prices and fewer rental units available on the market.
c. The shortage occurred because demand increased, and a new market equilibrium will feature higher rental prices and fewer rental units available on the market.
d. The shortage occurred because supply increased, and a new market equilibrium will feature lower rental prices and fewer rental units available on the market.
a
You might also like to view...
Under a balanced budget policy, a sharp decline in GDP will cause
a. no serious budget changes. b. a tax cut or an increase in expenditures. c. a tax increase or expenditure cut. d. tax receipts to exceed government expenditures.
For which pairs of goods is the cross-price elasticity most likely to be negative?
a. peanut butter and jelly b. automobile tires and coffee c. pens and pencils d. paperback novels and electronic books for e-readers
Fiat money has
A) little to no intrinsic value but is backed by the quantity of gold held by the central bank. B) little to no intrinsic value and is authorized by the central bank or governmental body. C) value, because it can be redeemed for gold by the central bank. D) a great intrinsic value that is independent of its use as money.
Refer to the diagram, where variable inputs of labor are being added to a constant amount of property resources. The total output of this firm will cease to expand:
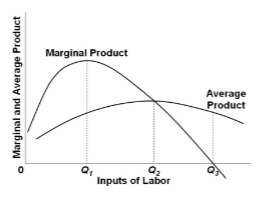
A. if a labor force in excess of Q 1 is employed.
B. if a labor force in excess of Q 2 is employed.
C. if a labor force in excess of Q 3 is employed.
D. only if the marginal product curve becomes negative at all levels of output.