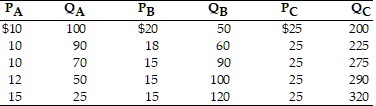
 Refer to the above table. Suppose the price of B rises from $18 to $20. What is the cross price elasticity of demand between A and B?
Refer to the above table. Suppose the price of B rises from $18 to $20. What is the cross price elasticity of demand between A and B?
A. +1
B. 0
C. -1
D. -2
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
When a U.S. firm sells a good abroad for, say, 100 euros (assume $1.5=1euro), U.S. net exports increase by $150. These $150 in exports can be accounted for as $150 increase in capital outflow because ________
A) private consumption in the foreign country increases by $150 B) if the U.S. firm uses the 100 euros to buy a share of stock in a foreign firm, the firm is supplying U.S. capital to that foreign firm C) if the U.S. firm uses the proceeds to buy a U.S. bond, capital investment in the foreign country has increased D) all of the above E) none of the above
When the price of a good changes, the total effect of the price change on the quantities purchased can be found by comparing the quantities purchased
A) on the old budget line and the new budget line. B) on the original indifference curve when faced with the original prices and when faced with the new prices. C) on the new budget line and a hypothetical budget line that is a parallel shift back to the original indifference curve. D) on the new indifference curve.
Under the Bretton Woods system, a country could alter its exchange rate
A) by changing its value relative to gold. B) whenever it determined that there was a fundamental disequilibrium. C) only when the IMF permitted due to a fundamental disequilibrium. D) under no circumstances.
During the 100 years before the Revolutionary war, shipping costs were reduced by nearly:
a. 10 percent. b. 25 percent. c. 50 percent. d. 70 percent. e. Shipping costs increased during that period.