Describe how these chemical reactions assist with blood sugar homeostasis: gluconeogenesis, glycogenolysis, and glycogenesis
What will be an ideal response?
Gluconeogenesis is a reaction in which the liver uses non-carbohydrates sources (such as fats and proteins) to produce glucose. Glycogenolysis is a reaction in which the liver breaks down stored glycogen and turns it into glucose. Both of these reactions response to hormones that are meant to raise blood sugar levels. Glycogenesis is a reaction in which the liver turns excess glucose in the blood into a large polysaccharide called glycogen. This type of reaction removes glucose from the blood and lowers blood sugar levels.
You might also like to view...
Hyperparathyroidism
A. causes bulging eyes and goiters. B. is detected by low blood calcium ion concentration. C. is most often caused by injury. D. is most often caused by a tumor.
The straight tubules in the testis lead into the
a) Efferent ducts b) Afferent ducts c) Rete testis d) Ductus epididymis e) Epididymis
Structure J is the
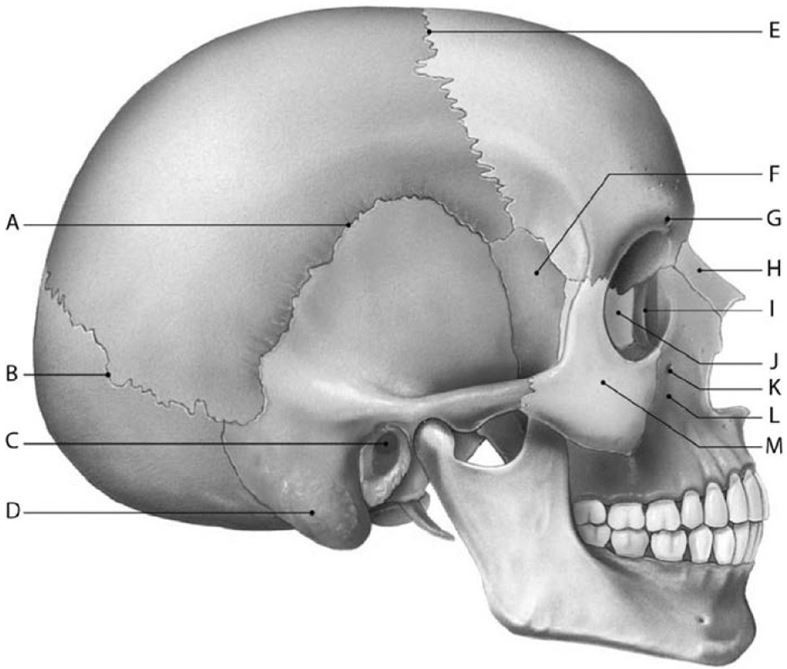
A) nasal.
B) lacrimal.
C) maxilla.
D) ethmoid.
E) palatine.
Type B intercalated cells are more active than Type A intercalated cells under normal circumstances, and their activity increases even more during acidosis
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false