When the price of coffee increases from $4 to $5 per pound, Elizabeth’s demand for coffee ______.
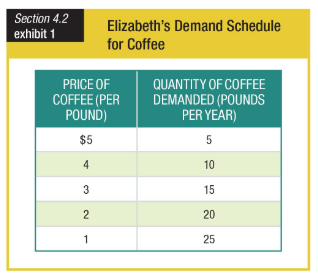
a. increases by 5 pounds
b. increases by 10 pounds
c. decreases by 5 pounds
d. decreases by 10 pounds
c. decreases by 5 pounds
You might also like to view...
A distributed lag regression
A) is also called AR(p). B) can also be used with cross-sectional data. C) gives estimates of dynamic causal effects. D) is sometimes referred to as ADL.
Suppose the price of beef declines by $0.50 per pound at the supermarket. Consumers of beef immediately increase their purchases of beef. This illustrates:
a. the fact that beef is an inferior good. b. the cross-elasticity effect of a price decrease. c. the substitution effect of a price decrease. d. the fact that beef is an economic bad. e. the income effect of a rise in price.
The price elasticity of demand is measured by the
A) percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price. B) percentage change in price divided by the percentage change in quantity demanded. C) change in quantity demanded divided by the change in price. D) change in price divided by the change in quantity demanded.
Refer to the information provided in Table 14.2 below to answer the question that follows. Table 14.2B's Strategy ?AdvertiseDon't Advertise??A's profit $100 millionA's profit $200 million?AdvertiseB's profit $100 millionB's profit $50 millionA's Strategy????Don'tA's profit $50 millionA's profit $75 million?AdvertiseB's profit $200 millionB's profit $75 millionRefer to Table 14.2. Firm A?s dominant strategy is
A. to advertise. B. dependent on what Firm B does. C. to not advertise. D. indeterminate from this information, as no information is provided on Firm A?s risk preference.