In the above figure, starting at E1, if there is a supply shock that is permanent, the
A) aggregate supply would shift to SRAS1 and LRAS1 would shift to LRAS0.
B) aggregate supply would shift to SRAS1 and LRAS0 would shift to LRAS1.
C) aggregate supply would shift to SRAS2 and LRAS0 would shift to LRAS1.
D) aggregate supply would shift to SRAS1 and then return to SRAS0.
Answer: C) aggregate supply would shift to SRAS2 and LRAS0 would shift to LRAS1.
You might also like to view...
The economy pictured in the figure below has a(n) ________ gap with a short-run equilibrium combination of inflation and output indicated by point ________. 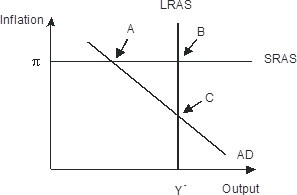
A. recessionary; B B. recessionary; C C. recessionary; A D. expansionary; A
An example of an underemployed resource is a(n)
a. farmer in Illinois who plants corn instead of wheat b. auto mechanic who is laid off from his job c. welfare recipient who doesn't work d. retired senior citizen who doesn't work e. person with a Ph.D. in chemistry who drives a taxi as a full-time job
If allocating dorm rooms changes from allocation by lottery to allocation by the market:
A. the allocation problem is still an economic problem. B. it becomes a political problem but not an economic problem. C. it becomes a social problem but not an economic problem. D. it becomes an economic problem.
The public debt is
A. the total value of all outstanding federal government securities. B. a situation in which the government's spending is exactly equal to the total taxes and other revenues it collects during a given time period. C. an excess of government spending over government revenues during a given time period. D. all federal government debt irrespective of who owns it.