It is possible for an individual to be genotypically one gender but appear to be the opposite gender. Suppose an individual is genotypically male (XY) but has developed as a female. Explain what has happened and when it might have happened
What will be an ideal response?
Although genotypic sex is determined at conception, the expression of the Y chromosome does not begin until week 6 of development, when the SRY region of the Y chromosome should be expressed in males. If this is not expressed, the individual will develop as a female, which is what occurred in this case.
You might also like to view...
The eyes of the fetus open during the ________ month of pregnancy
a. 4th b. 5th c. 7th d. 6th
Use Figure 50-4 to predict on which day of a 28-day menstrual cycle estrogen levels would peak
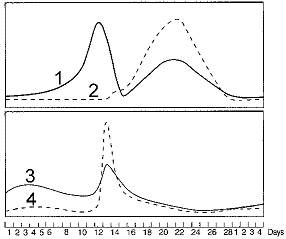
a. 10
b. 12
c. 14
d. 18
e. 22
Programmed cell death is called apoptosis. Indicate whether the statement is true or false
All of the following are examples of post-transcriptional regulation except
A) cells can regulate translation by affecting how readily ribosomes associate with mRNA to read it. B) in eukaryotic cells, small noncoding RNAs that work in post-transcriptional regulation include microRNAs and short interfering RNAs. C) cells can regulate translation by methylating certain DNA nucleotides. D) in prokaryotic cells, small noncoding RNAs that work in post-transcriptional regulation include small RNAs. E) cells can regulate how mRNA is spliced and exported out of the nucleus before translation occurs.