Perfectly inelastic demand means that consumers
A) are willing to buy any quantity of the good at a given price, but none at higher prices.
B) decrease their consumption as price rises.
C) increase their consumption as price rises.
D) will buy a certain quantity, regardless of price.
E) will buy a huge, almost infinite amount more, if the price falls just a little.
D
You might also like to view...
The typical labor supply curve is upward sloping but it is possible for the curve to be backward bending —negatively sloped—at very high wage levels. Which of the following would cause a backward-bending supply curve?
A) This would occur if leisure is an inferior good. B) This would occur when the substitution effect from an increase in the wage becomes larger than the income effect. C) This would occur when a large number of workers choose leisure rather than employment at low wages; only a very large increase in the wage will lead these workers to prefer employment to leisure. D) This would occur when the income effect from an increase in the wage becomes larger than the substitution effect.
Legislation that provides a subsidies for tobacco growers is an example of
a. public-interest legislation b. competing-interest legislation c. a positive-sum game d. special-interest legislation e. concentrated-costs legislation
The main reason that the deficit grows in a recession is that
a. the government reacts quickly and adjusts taxes to compensate. b. monetary policy that targets interest rates causes the costs of borrowing to fall. c. the deficit causes the recession, and reducing the deficit cures the recession. d. many forms of taxes act as automatic stabilizers.
Referring to Table 4.1, Box I should be filled with 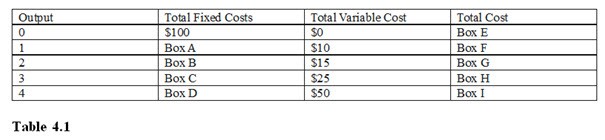
A. $150. B. $200. C. $115. D. $0.