Refer to Figure 4-3. At the equilibrium price of P1, consumers are willing to buy Q1 pounds of granola. Is this an economically efficient quantity?
A) Yes, because marginal cost is zero at the price of P1.
B) No, the marginal cost of the last unit (Q1 ) exceeds the marginal benefit of the last unit.
C) Yes, because P1 is the price where marginal benefit equals marginal cost.
D) No, the marginal benefit of the last unit (Q1 ) exceeds the marginal cost of that last unit.
C
You might also like to view...
When the price of broccoli increase relative to cauliflower, people who buy fresh vegetables respond by buying more cauliflower and fewer broccoli. As a result, the CPI has
A) a quality change bias. B) a new price bias. C) a commodity substitution bias. D) an outlet substitution bias. E) a new goods bias.
Does the Federal Reserve operate like an ordinary commercial bank? What is the Fed's job?
Figure 4-25
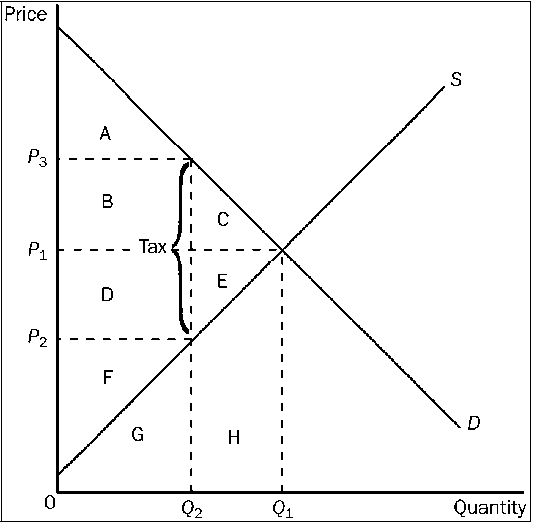
Refer to . The tax causes a reduction in consumer surplus that is represented by area
a.
A.
b.
B + C.
c.
D + E.
d.
F.
Quick Buck and Pushy Sales produce and sell identical products and face zero marginal and average cost. Below is the market demand curve for their product.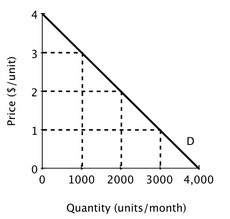 Suppose Quick Buck and Pushy Sales decide to collude and work together as a monopolist with each firm producing half the quantity demanded by the market at the monopoly price. If Quick Buck cheats by reducing its price to $1 and Pushy Sales matches the price cut, then if consumers are evenly split between the two firms, what will be Quick Buck's economic profit?
Suppose Quick Buck and Pushy Sales decide to collude and work together as a monopolist with each firm producing half the quantity demanded by the market at the monopoly price. If Quick Buck cheats by reducing its price to $1 and Pushy Sales matches the price cut, then if consumers are evenly split between the two firms, what will be Quick Buck's economic profit?
A. $3,000 B. $2,000 C. $1,000 D. $1,500