A researcher collects and analyzes narratives. During the coding process, they begin to see common themes around student study habits and then use those themes to better understand the motivations of how students study. This is an example of which type of data analysis?
A. case study
B. deductive analysis
C. inductive analysis
D. content analysis
Ans: C
You might also like to view...
Describe the instructional emphasis of a teacher using the essentialist curriculum
What will be an ideal response?
According to the text, curriculum principles may be viewed as all except:
a. half-truths b. whole truths c. partial truths d. hypotheses
Success with a task does not necessarily mean that a student possesses the skills necessary for repeated performance
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
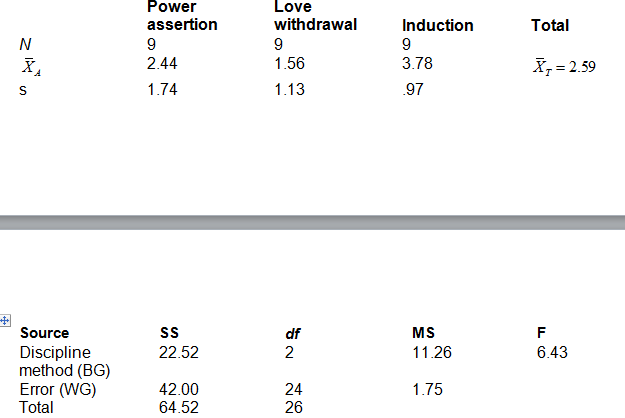
You decide to conduct the analytical comparison of Induction vs. Power assertion. Based on your calculations, which of the following represents the decision regarding the null hypothesis?
One part of raising children is having to discipline them. Hoffman (1963) described three common discipline methods used by parents: power assertion (use of punishment, force, taking away of privileges or possessions), love withdrawal (ignoring or refusing to speak to the child, explicitly stating a dislike for the child), and induction (reasoning with the child, communicating standards of behavior). Barnett, Quackenbush, and Sinisi (1996) noted that little attention had been given to children’s preferences for these different methods. From reviewing the literature, they hypothesized children express a greater preference for induction than power assertion, which in turn is preferred over love withdrawal.
They collected data from a sample of middle school students. Each student watched a videotape of a parent disciplining a child using one of the three forms of discipline. After viewing the videotape, each student rated the effectiveness of the discipline on a 1 to 5 scale, where 1 = “Not at all effective” and 5 = “Very effective”. The results of their analyses are presented below:
a. Do not reject H0 (p > .05)
b. Do not reject H0 (p < .05)
c. Reject H0 (p < .05)
d. Reject H0 (p < .01)