Consider the results from Model 2 in Table 1, above. Does an increase in W/S significantly increase, decrease, or have no effect on the government spending on health care (measured as the share of GDP)?
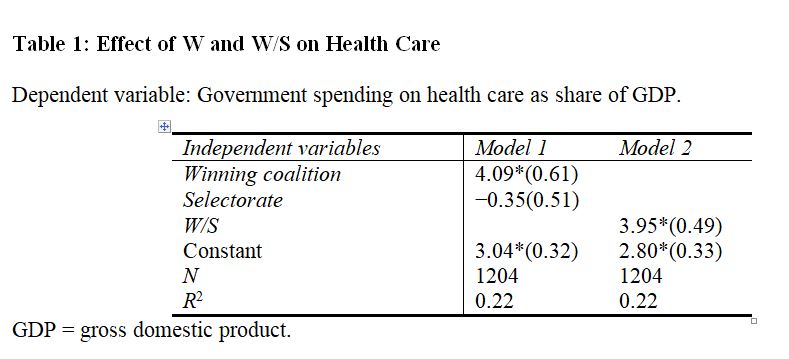
A. It significantly increases spending on health care.
B. It significantly decreases spending on health care.
C. It has no effect on health care spending.
A. It significantly increases spending on health care.
You might also like to view...
A form of government that emphasizes power sharing through guaranteed group presentation is referred to as ______.
A. federalism B. immobilism C. consociationalism D. confessionalism
Which of the following is a problem associated with the “bottom-up” approach to policy implementation?
A. The intent of the legislation is strictly adhered to. B. Political leaders have the duty to formulate policies promised to the public. C. Ease of implementation is not a necessary consideration for effectiveness. D. Field agents may be overly liberal in defining what is feasible, limiting available options.
All of the following are examples of the major social insurance programs in the United States except ______.
A. Social Security B. unemployment insurance C. worker’s compensation D. health flex plans
Parties are organized into various committees that range from national committees to precinct committees. Throughout history, parties have undergone realignments. Despite the dominant two-party system, third parties can influence the outcome of elections.
What will be an ideal response?