Which of the following are differences between cardiac and pulmonary rehabilitation?
1. Cardiac patients are typically younger.
2. Most cardiac patients are not able to walk for 1 hr.
3. Reimbursement is easier to obtain with cardiac rehabilitation.
4. Breathing exercises are not essential to cardiac patients.
a. 1 and 2 only
b. 2 and 3 only
c. 1, 3, and 4 only
d. 1, 2, and 3 only
ANS: C
Differences include disease focus, patient age (most cardiac patients will range from their late 30s on up to their 60s and 70s, while pulmonary patients, for the most part, will be 50 years or older), and exercises used within the program. Many cardiac patients will walk for up to 1 hr, while this may be virtually impossible for most respiratory patients. On the other hand, breathing exercises to improve ventilation are essential to the respiratory patient but are not that important to patients with cardiovascular diseases. Reimbursement variables between the two types of pro-grams also exist, with cardiac rehabilitation being more recognized by insurance payers.
You might also like to view...
How long should you hold your position while applying the standard release technique?
a. 5 to 10 seconds b. 15 to 25 seconds c. 30 seconds to 2 minutes d. 2 to 10 minutes
Which of the following is a way to prevent accidents with power saws?
A. Use whatever saw is most convenient B. Refuel gasoline-powered saws immediately C. Store blades and cutting chains separately D. Keep blades and cutting chains well sharpened
According to the National Institutes of Health, which of the following is TRUE?
A) Ovarian cancer is the seventh most common cancer among women. B) Ovarian cancer is the fifth most common cancer among women. C) Ovarian cancer causes more deaths than other female genital cancer because its symptoms are often attributed to other causes. D) Ovarian cancer is usually diagnosed only after it has metastasized. E) All are true except A.
The type of movement shown by the letter A is ____.
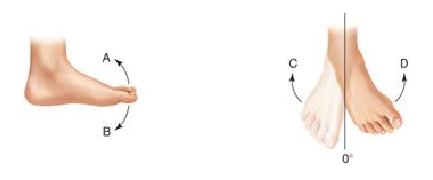
A. plantar flexion
B. dorsiflexion
C. internal rotation
D. eversion
E. inversion