Utility analysis helps economists understand
A) how people make decisions about what they buy and how much.
B) how to eliminate opportunity costs.
C) how to eliminate scarcity.
D) none of the above.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
The decision about whether to change prices frequently or infrequently is an application of the:
A. cost-benefit principle. B. scarcity principle. C. principle of comparative advantage. D. principle of increasing opportunity cost.
Consider the hypothetical supply and demand of Kidneys.
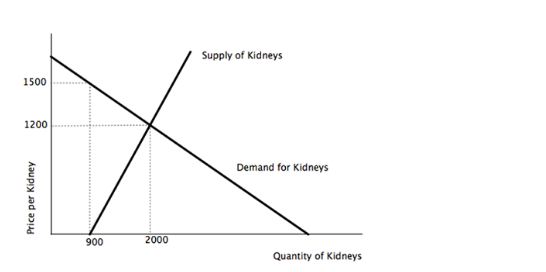
Initially, kidneys are exchanged by donations only (price=0). If the government decides to legalize kidney sales and the market reaches equilibrium, then:
A. total surplus increases.
B. consumer surplus remains the same.
C. producer surplus remains the same.
D. a shortage of kidneys will arise.
In 1990, U.S. nominal GDP was $5,744 billion and the GDP chain price index is 93.6 . Real GDP is:
a. $6,137 billion. b. $5,376 billion. c. $6,000 billion. d. $6,376 billion.
The “universal service” argument often requires that some products be sold at a loss while other products be sold at profits higher than normal.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)