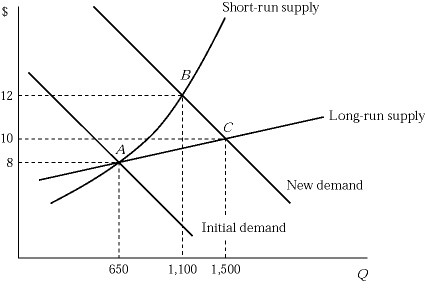
 Figure 9.5Figure 9.5 shows the short-run and long-run effects of an increase in demand of an industry. The market is in equilibrium at point A, where 100 identical firms produce 6 units of a product per hour. Suppose that the market demand curve shifts to the right. Why is the short-run supply curve steeper than the long-run supply curve?
Figure 9.5Figure 9.5 shows the short-run and long-run effects of an increase in demand of an industry. The market is in equilibrium at point A, where 100 identical firms produce 6 units of a product per hour. Suppose that the market demand curve shifts to the right. Why is the short-run supply curve steeper than the long-run supply curve?
A. Because production facilities are fixed in the short run.
B. Because each firm experiences diminishing returns in the short run.
C. Because production becomes costlier as firms squeeze more output from the existing production facilities.
D. All of these are correct.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Just because a firm can deter entry by a competitor does not mean it will deter entry.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Considering the concept of cross-price elasticity, if two goods are complements:
A. an increase in the price of one will cause a decrease in the demand for the other. B. an increase in the price of one will cause an increase in the demand for the other. C. a decrease in the price of one will cause a decrease in the demand for the other. D. the cross-price elasticity is positive.
Suppose there are three power-generating plants, each of which has access to 5 different production processes. The table below summarizes the cost of each production process and the corresponding number of tons of smoke emitted each.ProcessABCDE(smoke/day)(4 tons/day)(3 tons/day)(2 tons/day)(1 tons/day)(0 tons/day)Cost to Firm X ($/day)$500$514$530$555$585Cost to Firm Y ($/day)$400$420$445$480$520Cost to Firm Z ($/day)$300$325$360$400$550 Suppose the government imposes a tax of $21 on each ton of smoke emitted. To minimize costs, Firm X will emit ________ tons; Firm Y will emit ________ tons, and Firm Z will emit ________ tons.
A. 2; 3; 4 B. 3; 4; 4 C. 1; 2; 3 D. 1; 2; 4
The perpetual problem in economics is:
A. our inability to work together effectively. B. our inability to satisfy everyone's wants with the available resources. C. likely to be solved in resource-rich countries. D. our inability to utilize resources efficiently.